Juniperus scopulorum Sarg. syn. Sabina scopulorum (Sargent) Rydberg - Cupressaceae - Rocky Mountain juniper, Rocky Mountain redcedar, Rocky-Mountain-Wacholder
Small evergreen tree, native to western North America (West Canda to North Mexico); leaves light to dark green but often glaucous blue or blue-gray, whip leaves 3-6 mm, not glaucous adaxially, scalelike leaves 1-3 mm; seed cones globose, maturing in 2 years, appearing light blue when heavily glaucous, but dark blue-black beneath glaucous coating when mature. efloras.org
Juniperus scopulorum f. columnaris (Fassett) Rehder (cultivars 'Skyrocket', Blue Arrow') is a popular ornamental plant, grown for its very slender, strictly erect growth habit.
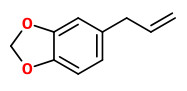
„The neutral leaf oil of Rocky Mountain juniper was analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography. D-sabinene was found to be the major constituent (45.7%) and smaller amounts of D-limonene (11.4%), D-α-pinene (4.2%), γ-terpinene (1.15%), p-cymene (1.4%), L-linalool (1.2%), D-terpinen-4-ol (2.9%), citronellol (0.2%), L-β-elemene (0.2-0.3%), three isomeric cadinenes (2.7%), L-elemol (6.0%), and safrole (1.85%) were isolated. α-Thujene, camphene, car-3-ene, myrcene, α-terpinene, terpinolene, thujone, isothujone, methyl citronellate, sabinyl acetate, sabinol, geraniol, α- and δ-cadinol, and trans-isoeugenol were tentatively identified.“
[„Gas-liquid chromatography of terpenes: Part XI. The volatile oil of the leaves of Juniperus scopulorum Sarg.“ Rudloff, E. von, and F. M. Couchman., Canadian Journal of Chemistry, Vol.42.8, 1964, 1890-1895]
„The oil of J. scopulorum is virtually devoid of the cadinol type sesquiterpenes but differentiation from that of J. virginiana is difficult. A useful measure of clinal variation within different populations of each species is the ratio of sabinene and limonene percentages. The occurrence of aromatic ethers in J. scopulorum and J. virginiana is erratic; in J. horizontalis they are present in trace amounts only.“
[Von Rudloff, Ernst. „Chemosystematic studies of the volatile oils of Juniperus horizontalis, J. scopulorum and J. virginiana.“ Phytochemistry 14.5-6 (1975): 1319-1329]
Main components of the steam distilled wood oil from of J.scopulorum (3.4%) were thujopsene (57.9%), cuparene (6.1%), and cedrol (6.1%), accompanied by α-cedrene (4.3%), widdrol (3.0%), and β-cedrene (2.4%).
[Investigation of Juniperus species of the United States for new Sources of Cedarwood Oil., Adams, R.P., Economic Botany, 41(1), 1987, 48-54]
Main components of the steam distilled essential oil of the leaves of J.scopulorum were β-pinene (5.1-9.2%), myrcene (2.6-4.8%), limonene (5.9-36.6%), and bornyl acetate (0.3-22.1%). Safrole was not present in the oil, but found in J.virginiana oils.
[Cantrell, Charles L., et al. „Podophyllotoxin and essential oil profile of Juniperus and related species.“ Industrial Crops and Products 43 (2013): 668-676] PDF
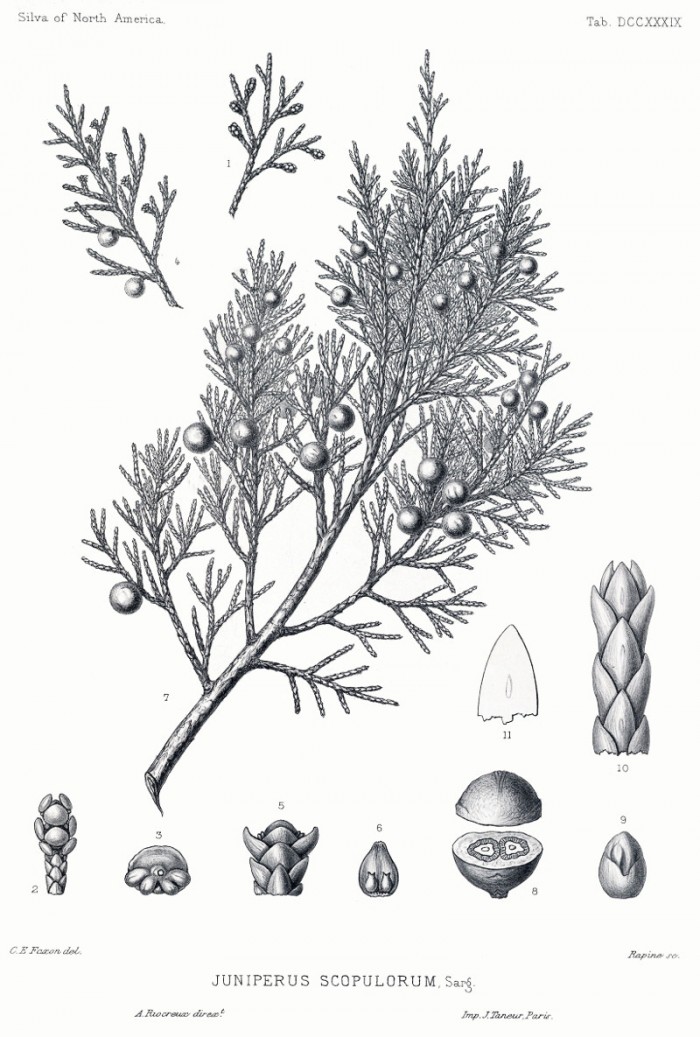
Sargent,C.S., The Silva of North America, vol.14, t.739 (1898) [C.E.Faxon]
plantgenera.org
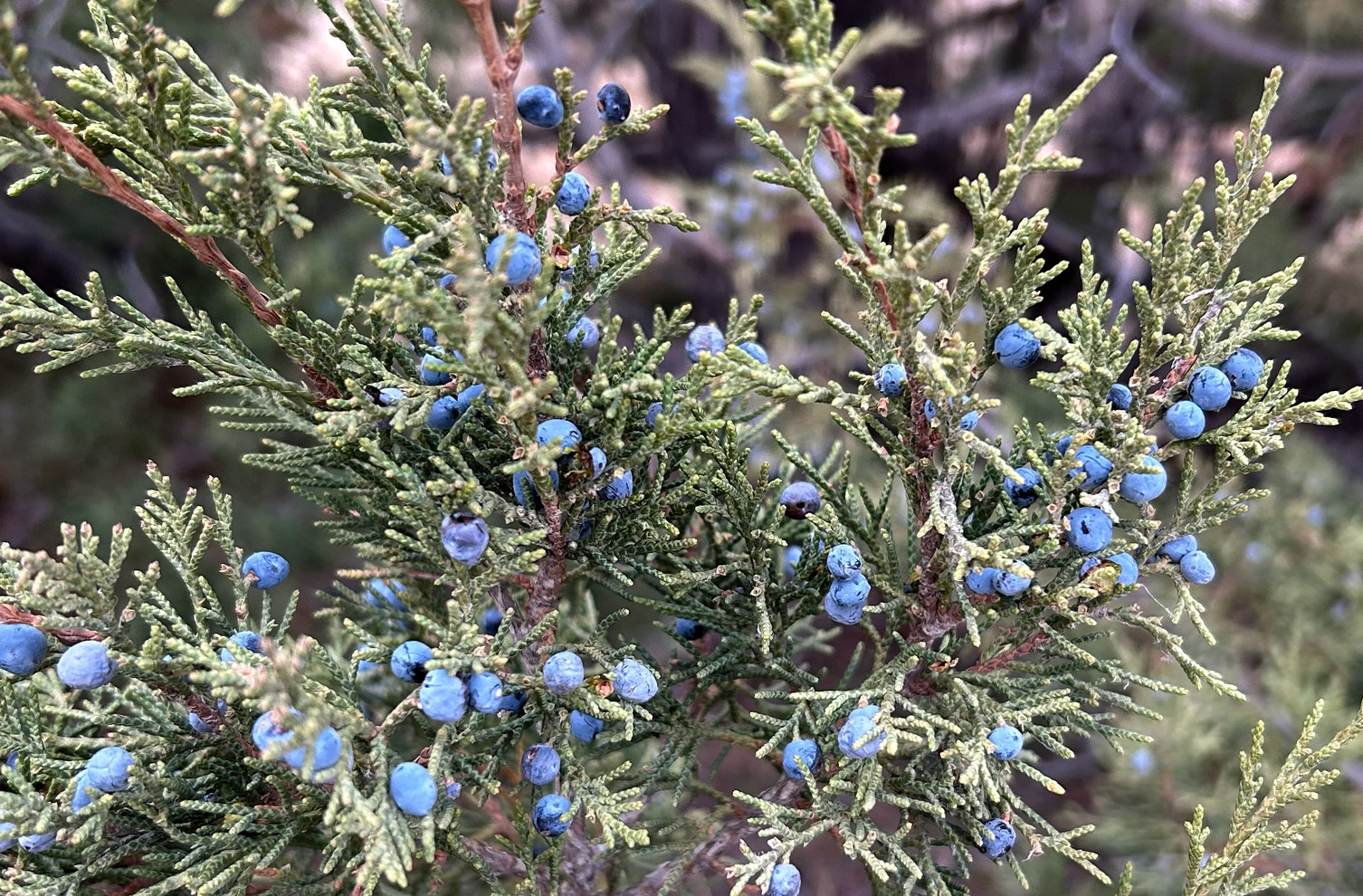

Juniperus scopulorum, Notch Trail, USA (2025) © Lane Keller CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org