Rosa multiflora Thunb. - Rosaceae - multiflora rose, Japanese rose, Vielblütige Rose
Petals white; flowers 1.5–2 cm in diam. - Rosa multiflora var. multiflora
Petals pink; flowers to 4 cm in diam. - Rosa multiflora var. cathayensis
Climbing shrub, native to Japan, Korea, China; grown as an ornamental plant and also used as a rootstock for grafted ornamental rose cultivars; curved prickles paired below leaves, sometimes absent; leaves including petiole 5-10cm long; leaflets usually 5-9, obovate, oblong, or ovate, abaxially pubescent, adaxially glabrous; flowers numerous in corymb, 1.5-4cm in diam.; pedicel 1.5-2.5 cm, sepals 5, deciduous, lanceolate; petals 5, semi-double or double, white, pinkish, or pink (in some cultivated plants), fragrant
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200011286
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rosa_multiflora
Rose multiflora var. cathayensis was found to contain eugenol (22.8%) and 2-phenylethanol (18.1%) as main components of the floral absolute oil.
[Dun-yuan, Xue, Li Zhao-lin, and Chen Yao-zu. „Studies on Chemical Ingredients of the Floral Absolute Oil of Rose Multiflora. Cathayensis.“ Chemical Research In Chinese Universities (1991): 08]
Main components of the petroleum ether fraction of R. multiflora Thunb. hips were acids like dodecanoic acid (8.7%), hexadecanoic acid (9.2%), linoleic acid (26.0%), oleic acid (22.5), and stearic acid (6.3%). Olfactorly interesting are linalool (2.3%) and methyleugenol (1.8%).
„The petroleum ether fraction (PEF) was identified to be the active fraction in inflammation animal models… Down-regulating COX-2 expression and reducing NO production through inhibiting iNOS activity may be the partial mechanism of the action of PEF. GC–MS analysis indicated enriched unsaturated fatty acids may be responsible for the anti-inflammatory activity of PEF and this herb. This study provided pharmacological and chemical basis for the application of the hip of R. multiflora Thunb. in inflammatory disorders.“
[Guo, Dejian, et al. „Anti-inflammatory activities and mechanisms of action of the petroleum ether fraction of Rosa multiflora Thunb. hips.“ Journal of Ethnopharmacology 138.3 (2011): 717-722]
Main volatiles of the flower scent of R.multiflora var. cathayensis were citronellol (41.9%), 2-phenylethanol (15.6%), and α-pinene (13.4%).
[Ajun, Guo, and Li Limin. „Composition and antibacterial effect of volatile organic compounds of Rosa multiflora var. cathayensis.“ Journal of Northeast Forestry University (2016): 11]
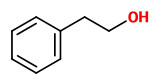
Rosa multiflora flowers predominantly produce 2-phenylethanol but not 3,5-dimethoxytoluene (DMT) or 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene (TMB).
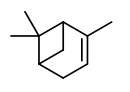
„Although several genes encoding linalool, nerolidol, or α-pinene synthase homologues were found here, these compounds are not known to produce in R. multiflora flowers.“
[Nakamura, Noriko, et al. „Genome structure of Rosa multiflora, a wild ancestor of cultivated roses.“ Dna Research 25.2 (2018): 113-121]
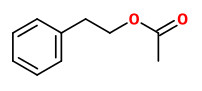
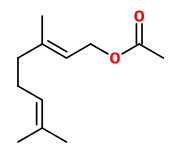
The volatiles released by Rosa multiflora flowers were mainly geranyl acetate and phenylethyl acetate.
[Lv, Yang, et al. „Effects of flower volatiles from two liana species on spontaneous behavior of mice.“ Acta Ecologica Sinica 40.1 (2020): 90-96]
Rosa multiflora, Donauinsel (Reichsbrücke - Praterbrücke) © Rolf Marschner (2006)
http://botanische-spaziergaenge.at/viewtopic.php?f=411&t=1224