Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Picea mariana (Mill.) Britton et al. - syn. Abies mariana Mill. - Pinaceae
black spruce, bog spruce, Schwarzfichte
Eevergreen coniferous tree, up to 15m tall, native to North America (Canada).
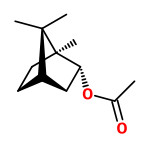
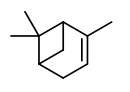
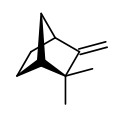
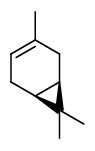
The steam-distilled essential oil of the foliage contained bornyl acetate (34.2%) as main component, together with α-pinene (12.9%), and camphene (16.4%). Minor components were δ-3-carene (5.8%), limonene (4.1%), myrcene (3.7%), β-pinene (2.6%), β-phellandrene (1.0%), isoborneol (0.1%), terpinen-4-ol (0.4%), α-terpineol (1.2%), and trans-carveol (0.1%). Main components found in the hydrosol were α-terpineol, borneol, bornyl acetate, (Z)-3-hexenol, camphenehydrate, and 1.8-cineole.
[Garneau, François-Xavier, et al. „Chemical Composition of the Hydrosol and the Essential Oil of Three Different Species of the Pinaceae Family: Picea glauca (Moench) Voss., Picea mariana (Mill.) BSP, and Abies balsamea (L.) Mill.“ Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants 15.2 (2012): 227-236]
„Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) of Abies balsamea, Picea mariana and Tsuga canadensis leaf essential oils assigned bornyl acetate as a major peak in A.balsamea and P.mariana, while isobornyl acetate was identified as the major peak in T.canadensis. Though these two isomers elute closely on GC, their characteristic mass spectra allow unequivocal structural assignment…
[Bernart, Matthew W. „Closely eluting bornyl and isobornyl acetates are chemotaxonomic markers in the Pinaceae by virtue of their unique mass spectra.“ American Journal of Essential Oils and Natural Products 4.2 (2016): 41-46] http://www.essencejournal.com/vol4/issue2/pdf/4-3-1.1.pdf
“…the essential oil of Black spruce (Picea mariana) bark residue was obtained using two types of hydrodistillations: steam distillation (SD) and water distillation (WD). Both gave similar yields and compositions as analyzed using gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. The essential oil composition is turpentine-like with the predominance of α-pinene (40.6% SD; 40.5% WD) and β-pinene (33.9% SD; 25.9% WD), followed by hydrocarbon monoterpenes β-phellandrene (4.8% SD; 3.6% WD), 3-carene (4.1% SD; 3.1% WD), and limonene (4.0% SD; 3.7% WD). Hydrosol’s composition is rich in oxygenated compounds with α-terpineol (29.3% SD; 33.5% WD), trans-pinocarveol (5.2% SD; 3.7% WD), terpinen-4-ol (5.0% SD; 5.8% WD), verbenone (4.9% SD; 5.4% WD), borneol (4.9% SD; 3.9% WD), and pinocarvone (4.6% SD; 4.3% WD). These black spruce bark essential oils differ in composition from those from needles, which are commercially available and rich in bornyl acetate.„
[Francezon, Nellie, and Tatjana Stevanovic. „Chemical Composition of Essential Oil and Hydrosol from Picea mariana Bark Residue.“ BioResources 12.2 (2017): 2635-2645]
Picea mariana (Miller) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb.
Sargent, C.S., The Silva of North America, vol.12 t.596 (1898) [C.E. Faxon]
http://botanicalillustrations.org/species.php?id_species=789192
Picea mariana
© Rolf Marschner (2015),
www.botanische-spaziergaenge.at