Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich. - Annonaceae - Ethiopian pepper, Grains of Selim, Senegal pepper, negro pepper
Mohrenpfeffer, Senegalpfeffer, Selimskörner, Kanipfeffer
Evergreen tree, 15-30m tall, native to Africa; bark grey-brown; branches red-brown to blackish; leaves oblong-elliptic to ovate, 8-16.5cm long, leathery, bluish-green and hairless above, covered in brown appressed hairs below, margin entire; petiole short and thick, usually dark-coloured; flowers solitary or in clusters of 2-5, greenish-white to yellow, strongly scented; fruit of many cylindric carpels, up to 6 cm long, green or reddish.
https://www.zambiaflora.com/speciesdata/species.php?species_id=123860
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Xylopia+aethiopica
„Aromatic, quite pungent and slightly bitter, comparable to a mixture of cubeb pepper and nutmeg… Negro pepper is often smoked during the drying process which results in an attractive smoky-spicy flavour.“
http://gernot-katzers-spice-pages.com/engl/Xylo_aet.html
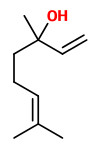
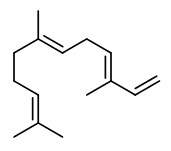
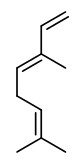
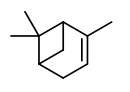
Main components among the forty one compounds characterized by GC/MS in Xylopia aethiopica oil obtained by hydrodistillation of dried fruits collected in Benin (West Africa) were sabinene (36.0%), 1,8-cineole (12.8%), linalool (3.9%), and terpinen-4-ol (7.0%).
[Poitou, Frédéric, et al. „Composition of the essential oil of Xylopia aethiopica dried fruits from Benin.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 8.3 (1996): 329-330]
AEDA of a solvent extract of the ground, dried, smoked fruits of Xylopia aethiopica (extracted with solvent mixture of methanol, water, and dichloromethane, 2-4.5%) showed linalool (FD 8192) to be the most intense component giving the pepperish note. The other most important odorants present in the volatile oil of the fruit were (E)-β-ocimene (flowery, FD 2048), α-farnesene (sweet flowery, FD 2048), β-pinene (terpeny, FD 512), α-pinene (terpeny, FD 1024), myrtenol (flowery, FD 512), and β-phellandrene (terpeny, FD 128). Non-terpenic odor-active compounds were 3-ethylphenol (phenolic, FD 128), vanilline (vanilla, FD 128), hexanoic acid (acidic, FD 8), and 4-ethyl-2-methoxyphenol (smoky, FD 4). The phenolic odor of 3-ethylphenol and the vanilla-like of vanilline are very easily noticed during the sniffing experiments even though these compounds appeared only in traces.
[Tairu, A. O., T. Hofmann, and P. Schieberle. „Identification of the key aroma compound in dried fruits of Xylopia aethiopica.“ PerspectiVes on new crops and new uses (1999): 474-478] https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/proceedings1999/pdf/v4-474.pdf
The main constituents identified in the essential oil from the dried fruits of X.aethiopica growing in Sudan were 4-terpineol (11.3%), β-pinene (6.1%), α-terpineol (6.0%), 1,8-cineole (5.4%), cis-α-copaen-8-ol (4.6%), 13-epimanoyl oxide (4.6%), spathulenol (4.2%), pinocarveol (3.2%), myrtenol (2.9%), o-cymene (2.8%), eudesma-1,3-dien-11-ol (2.3%), eudesma,4-11(13)-dien-2-ol (2.3%), cuminic alcohol (2.2%), kaur-16-ene (2.2%) and α-pinene (1.8%).
[Elhassan, Itmad Awad, Elmubarak Elsiddig Elamin, and Saad Mohamed Hussein Ayoub. „Chemical composition of essential oil in dried fruits of Xylopia aethiopica from Sudanfr.“ Open Access Journal of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants 1.1 (2010): 24]
Main components of the essential oil (hydrodistillation, 1-8%) of four samples of X.aethiopica growing at different sites in Cameroun were α-pinene (3.3-13.6%), β-pinene (8.2-44.1%), β-phellandrene+1,8-cineole (coeluting, 8.7-31.2%), terpinen-4-ol (1.5-4.5%), α-copaene (0.5-3.7%), and germacrene D (3.6-5.3%).
[Noudjou, Félicité, et al. „Composition of Xylopia aethiopica (Dunal) A. Rich essential oils from Cameroon and identification of a minor diterpene: ent-13-epi manoyl oxide.“ Biotechnologie, Agronomie, société et environnement 11.3 (2007): 193-199] http://www.pressesagro.be/base/index.php/base/article/viewFile/326/313
The major constituents of the essential oil extracted (4.4%) from air-dried fruits of X.aethiopica harvested in Togo were β-pinene (23.6%), α-pinene (11%), sabinene (9.8%), germacrene D (8.3%) and 1,8-cineole (8.2%).
[Koba, Koffi, et al. „Chemical composition and in vitro cytotoxic activity of Xylopia aethiopica (Dun) A. Rich.(Annonaceae) fruit essential oil from Togo.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 20.4 (2008): 354-357]
„Xylopia aethiopica (eru) seeds have an aromatic pungent taste and dried fruits are important as flavourings to prepare local soups in West Africa. Medicinally, the fruit is used to treat cough, stomachache, dizziness, amenorrhea, bronchitis and dysentery. The fruits mixed with roots are used in the treatment of rheumatism.“
[Dada, Ajibola Abisoye, Beatrice Olawumi Temilade Ifesan, and Juliet Fatmata Fashakin. „Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of selected local spices used in “Kunun” beverage in Nigeria.“ Acta Scientiarum Polonorum Technologia Alimentaria 12.4 (2013): 373-378] https://www.food.actapol.net/pub/4_4_2013.pdf

Xylopia aethiopica fruits, Odzala-Kokoua National Park, Congo (2025)
© Gwili Gibbon CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org