Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Santalum paniculatum Hook. & Arn. - Santalaceae - ʻIliahi (Hawaiian), mountain sandalwood, Hawaiian sandalwood
Shrub or tree, endemic only on the island of Hawaii, also called “The Big Island”; flowers green-whitish
„Flowers are mildly scented to unscented, but the heartwood is very fragrant in 30+ years old trees… From the 1790's to mid-1830's, ʻiliahi and the Hawaiian people who harvested the logs experienced an incredible hardship with the exportation of sandalwood.. Many thousands of Hawaiians, at the order of the aliʻi, under Kamehameha I (the Great), left off agriculture and worked to supply the Sandalwood Trade. The consequences were devastating.“
http://nativeplants.hawaii.edu/plant/view/Santalum_paniculatum_paniculatum
lit. cit. e.g. [„Traditional Trees of the Pacific Islands“ by Craig R. Elevitch, pages 698, 699, 703, 710, 712]
„Today, at least four sandalwood species and several varieties are known on the Hawaiian Islands, while other taxonomic revisions suggested up to six species: S. involutum H. St.John, S. pyrularium A. Gray, S. reycinetianum Gaudich., S.haleakalae Hillebr., S. ellipticum Gaudich. and S. paniculatum Hook. & Arn. … S. paniculatum is the only Hawaiian sandalwood species that is currently commercially harvested, in very limited quantities, and conservation efforts are being introduced… olfactory analysis revealed that all four oils [two oils steam-distilled from heartwood, the other two oils steam-distilled from butt-wood and rectified] elicit an impactful fresh sweet-woody, floral, oily-nutty, balsamic odor reminiscent of East Indian sandalwood oil but less creamy-milky, animalic and slightly weaker. The dry-down was being described as rich-woody, milky and floral with similar tenacity compared with the oil from S. album, but overall it was weaker and less radiant.
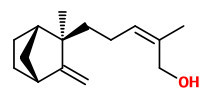
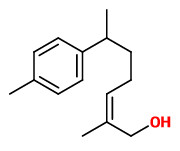
(Z)-α-santalol was the predominant compound ranging between 34.5% and 40.4%. Further main constituents characterized in quantities greater on average than 1.5% were (Z)-β-santalol (11.0-16.2%), (Z)-nuciferol
(3.3-6.7%), (Z)-trans-α-bergamotol (3.2-4.8%), epi-β-santalol (2.6-4.2%), (Z)-lanceol (2.0-4.6%), (E)-α-santalal (1.8-2.9%), (Z)-β-curcumen-12-ol (1.4-3.4%), spirosantalol (1.6-2.4%) and (Z)-ɣ-curcumen-12-ol (0.9-2.4%).“
[Braun, Norbert A., et al. „Hawaiian sandalwood: oil composition of Santalum paniculatum and comparison with other sandal species.“ Natural product communications 9.9 (2014): 1934578×1400900936.] https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1934578X1400900936
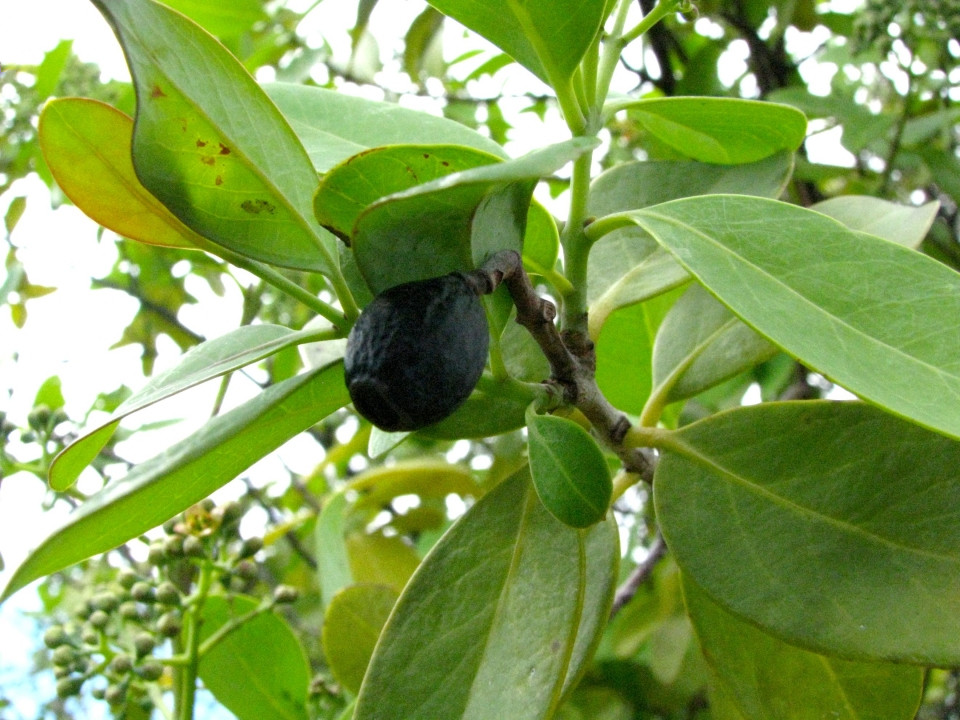

Santalum paniculatum fruit. Hawaiʻi, USA
CC BY-SA 2.0, Author: David Eickhoff Useful Tropical Plants - Santalum paniculatum Images