Santalum paniculatum Hook. & Arn. - Santalaceae - ʻIliahi (Hawaiian), mountain sandalwood, Hawaiian sandalwood
Shrub or tree, endemic only on the island of Hawaii, also called “The Big Island”; flowers green-whitish
„Flowers are mildly scented to unscented, but the heartwood is very fragrant in 30+ years old trees… From the 1790's to mid-1830's, ʻiliahi and the Hawaiian people who harvested the logs experienced an incredible hardship with the exportation of sandalwood.. Many thousands of Hawaiians, at the order of the aliʻi, under Kamehameha I (the Great), left off agriculture and worked to supply the Sandalwood Trade. The consequences were devastating.“
http://nativeplants.hawaii.edu/plant/view/Santalum_paniculatum_paniculatum
lit. cit. e.g. [„Traditional Trees of the Pacific Islands“ by Craig R. Elevitch, pages 698, 699, 703, 710, 712]
„Today, at least four sandalwood species and several varieties are known on the Hawaiian Islands, while other taxonomic revisions suggested up to six species: S. involutum H. St.John, S. pyrularium A. Gray, S. reycinetianum Gaudich., S.haleakalae Hillebr., S. ellipticum Gaudich. and S. paniculatum Hook. & Arn. … S. paniculatum is the only Hawaiian sandalwood species that is currently commercially harvested, in very limited quantities, and conservation efforts are being introduced… olfactory analysis revealed that all four oils [two oils steam-distilled from heartwood, the other two oils steam-distilled from butt-wood and rectified] elicit an impactful fresh sweet-woody, floral, oily-nutty, balsamic odor reminiscent of East Indian sandalwood oil but less creamy-milky, animalic and slightly weaker. The dry-down was being described as rich-woody, milky and floral with similar tenacity compared with the oil from S. album, but overall it was weaker and less radiant.
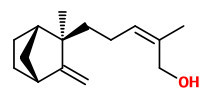
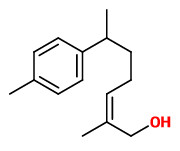
(Z)-α-santalol was the predominant compound ranging between 34.5% and 40.4%. Further main constituents characterized in quantities greater on average than 1.5% were (Z)-β-santalol (11.0-16.2%), (Z)-nuciferol
(3.3-6.7%), (Z)-trans-α-bergamotol (3.2-4.8%), epi-β-santalol (2.6-4.2%), (Z)-lanceol (2.0-4.6%), (E)-α-santalal (1.8-2.9%), (Z)-β-curcumen-12-ol (1.4-3.4%), spirosantalol (1.6-2.4%) and (Z)-ɣ-curcumen-12-ol (0.9-2.4%).“
[Braun, Norbert A., et al. „Hawaiian sandalwood: oil composition of Santalum paniculatum and comparison with other sandal species.“ Natural product communications 9.9 (2014): 1934578×1400900936.] https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1934578X1400900936
„In routine testing, a small percentage (0.1-2.4%) of people have been found to be allergic to album oil. However, in many of these studies, the provenance, purity, and source of the sandalwood is not clear. For example, other species of sandalwood, such as Western Australian (Santalum spicatum) or Hawaiian sandalwood (Santalum paniculatum), contain significant percentages of farnesol, an irritant, that is not found in oil from S. album.“
[Moy, Ronald L., and Corey Levenson. „Sandalwood album oil as a botanical therapeutic in dermatology.“ The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology 10.10 (2017): 34] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5749697/

Santalum paniculatum, Hawaii (2025) © Adrian Burke CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org
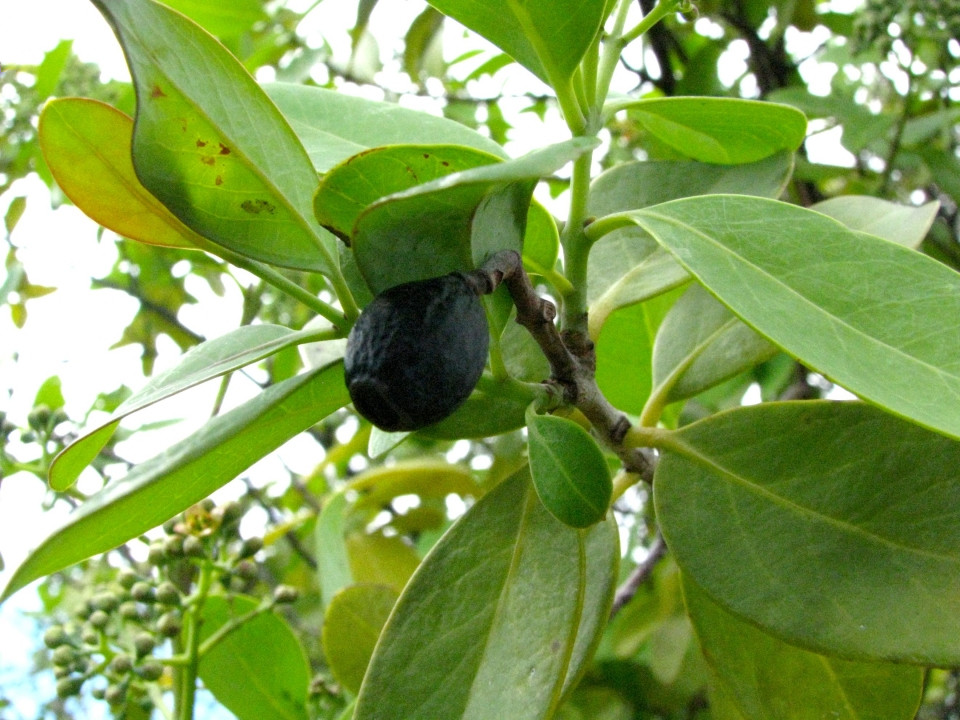

Santalum paniculatum fruit. Hawaiʻi, USA CC BY-SA 2.0, Author: David Eickhoff Useful Tropical Plants - Santalum paniculatum Images