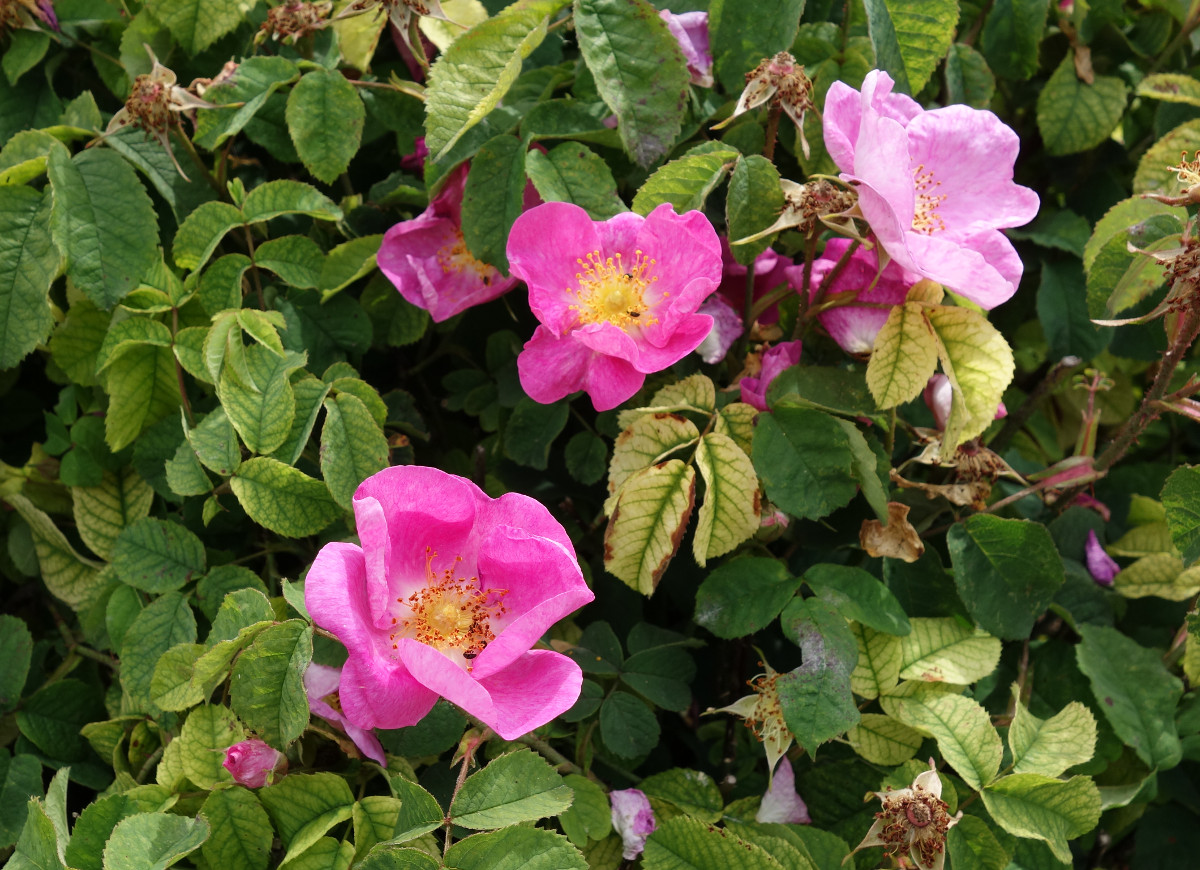
Rosa gallica L. - syn.Rosa gallica var. officinalis Thory - Rosaceae - apothecary rose, Essig-Rose, Apotheker-Rose
Erect deciduous shrub, stems many, with almost straight prickles and more abundant acicles; leaves with 2-3 pairs of leaflets, leaflets broadly elliptic, glabrous and usually deep green and slightly shining above, margins 1-2-serrate, with glandular hairs; flowers clustered 1-3, fragrant, petals 20-30mm long, broadly obovate, rose, crimson or purplish rose.
[Flora of New Zealand] http://www.nzflora.info/factsheet/Taxon/Rosa_gallica.html
„Little is known about the further history of the rose after the fall of the Roman Empire. Around 800 AD, in the Capitulare de villis of Charlemagne, roses are recommended for cultivation. At that time, roses were used as medicinal plants. In particular, the petals of the apothecary rose (R. gallica 'Officinalis') were used against diarrhea, as a gargle and as baths for poorly healing wounds.“
http://www.uni-ulm.de/fileadmin/website_uni_ulm/botgart/Bilder/Rosarium/rosenfaltblatt.pdf
The pale pink flowers of the famous old French rose, R.gallica hybrid 'Duchesse de Montebello' (Laffay, France, 1829) give off a fresh-floral rosy scent of the May rose type. Main components of the headspace are phenylethanol (30.4%), phenylethyl acetate (6.9%), citronellol (6.0%), nerol (3.8%), myrcene (7.6%), α-pinene (5.8%), and β-caryophyllene (4.2%).
[Brunke, Ernst‐Joachim, Franz‐Josef Hammerschmidt, and Gerhard Schmaus. „Scent of roses–recent results.“ Flavour and fragrance journal 7.4 (1992): 195-198]
Main components of the headspace of Rosa gallica flowers collected on Tenax were alcohols like phenylethanol (41.8%) and nerol (2.6%), esters like geranyl acetate (18.1%) and phenylethyl acetate (7.7%), and sesquiterpenes like germacrene D (4.4%), and bourbobene (2.1%).
[Flament, I., C. Debonneville, and A. Furrer. „Volatile constituents of roses: characterization of cultivars based on the headspace analysis of living flower emissions.“ chapter in: Volatile compounds from Flowers, Teranishi, R.;Buttery, R. G.;Sugisawa, H. Bioactive volatile compounds from plants. (Book) 1993, 269-281]
Pentane/dichloromethane extracts of Rosa gallica petals showed phenylethanol as the main component (highest content of all old roses, up to 89.9%), followed by hydrocarbons (up to 28.5%). Other components were benzyl alcohol (0.2-10.6%), nerol (0-18.6%), geraniol (0.1-30.6%), geranyl acetate (0-4.4%), benzyl benzoat (0.1-1.0%) and nonanal/cis-rose oxide (0-0.2%). 4-Vinylphenol (0.2-10.6%) was detected in two samples of Rosa gallica.
[Characterization of 24 old garden roses from their volatile compositions., Antonelli, A., Fabbri, C., Giorgioni, M.E., Bazzocchi, R., Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45(11), 1997, 4435-4439]
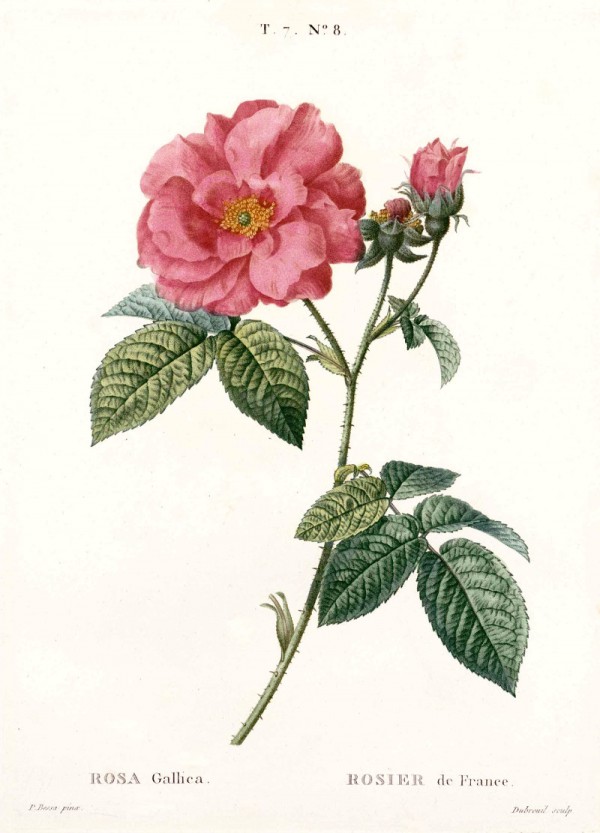

Duhamel du Monceau,H.L., Traité des arbres et arbustes, Nouvelle édition [Nouveau Duhamel], vol.7 t. 8 (1819) [P.Bessa]
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=1261457
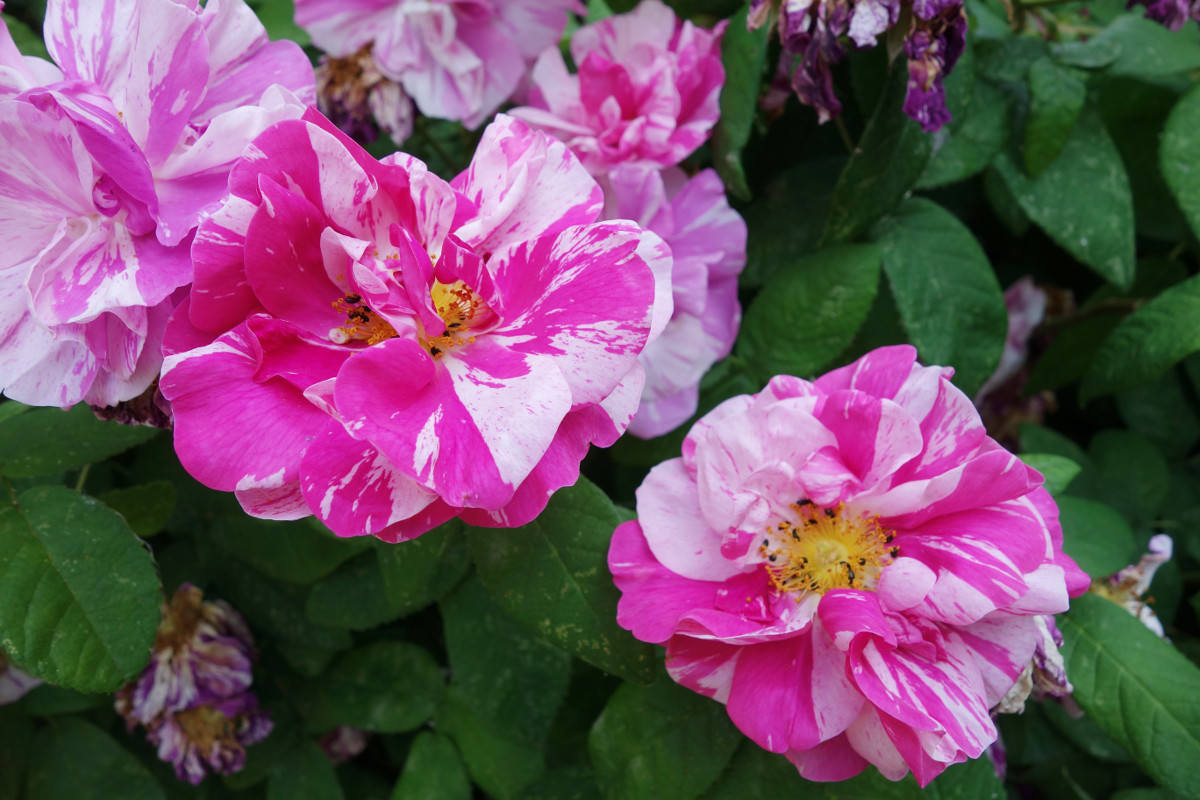

Apotheker-Rosen, CC BY-SA 3.0, Author: Andreas Kraska