Rosa × centifolia - Rosaceae - provence rose, Rose de Mai, cabbage rose, Provence-Rose, Zentifolie, Kohl-Rose
Old hybrid rose developed by Dutch rose breeders in 16th and 17th century; flowers globular, petals numerous, pink, white or dark red, highly scented; cultivated in Egypt, France (Provence: Grass) and Morocco.
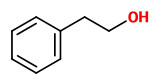
Pentane/dichloromethane extracts of Rosa x centifolia petals showed phenylethanol as the main component (56-86%), followed by hydrocarbons (8.5-23.5%). Other components were benzyl alcohol (0.8-4.9%), nerol (1.0-4.9%), geraniol (0.7-13.6%), geranyl acetate (0.2-1.6%), benzyl benzoate (0.1-0.7%), octanal (0.01-0.1%), and nonanal/cis-rose oxide (0.01-0.09%). „The composition of the four samples of R. × centifolia can be divided into two classes. Compared to roses 8 and 11, roses 9 and 10 were characterized by lower contents of nerol, geraniol, and geranyl acetate. The similarity of roses 9 and 10 is genetical: rose 10 (Old Pink Moss) was derived by a mossed mutation of rose 9 (R. centifolia). No other compounds stood out, and the differences among four R. centifolia cultivars and all other cultivars were of the same amplitude.“
[Characterization of 24 old garden roses from their volatile compositions., Antonelli, A., Fabbri, C., Giorgioni, M.E., Bazzocchi, R., Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 45(11), 1997, 4435-4439]
R.centifolia flower absolute (CAS 84604-12-6) is made from concrete oil (petrol ether extract of the rose petals) by dissolving in a minimum volume of absolute alcohol to remove the natural waxes and then distill the alcohol off (and finally bubbling nitrogen gas through the residue).
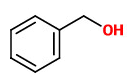
Rosa centifolia petals produced 0.225% concrete oil and 0.128% absolute oil. Analysis of the essential oil of R. centifolia showed phenylethanol (43.0%), geranyl acetate (15.6%), geraniol (10.5%) and linalool (6.9%) as major components. Benzyl alcohol (3.3%), benzaldehyde (1.5%) and citronellyl acetate (0.3%) were minor constituents beside unidentified compounds.
[Physico-chemical analysis and determination of various chemical constituents of essential oil in Rosa centifolia. Shabbir, M.K., Nadeem, R., Mukhtar, H., Anwar, F., Mumtaz, M. W., Pak. J. Bot, Vol.41(2), 2009, 615-620] http://pakbs.org/pjbot/PDFs/41%282%29/PJB41%282%29615.pdf
Application of GC-HRMS to rose absolutes of R.centifolia and R.damascena confirmed the identification of 19 new esters like the linoleates and linolenates of phenylethanol, citronellol, nerol and geraniol. „With these identified esters, the known volatile fraction of rose absolute increased from 90 percent to 92.“
[Remy, Pierre‐Alain, et al. „Identification of novel compounds in rose absolute with gas chromatography/high‐resolution mass spectrometry.“ Flavour and Fragrance Journal 37.3 (2022): 133-143]
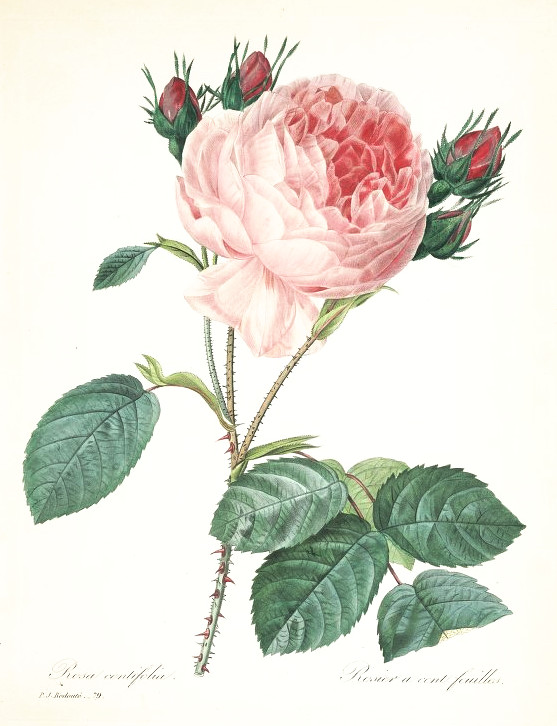

Redouté, P.J., Choix des plus belles fleurs et des plus beaux fruits, t.79 (1833) [P.J. Redoute]
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=1260556
Rosa × centifolia ‚Muscosa‘ (Rosa ×centifolia forma muscosa; Moosrose)
„Parsley-like curled, green leaf outgrowths and the oil glands make the calyx and flower stalks look like moss. This moss - especially the bud that opens up - is what makes this rose so attractive. The resin, which is sticky to the touch, smells very spicy when the leaves and stems are rubbed between the fingers.“ https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moosrose
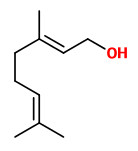
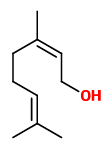
Main components of the headspace of Rosa muscosa purpurea flowers collected on Tenax were phenylethanol (29.9%), geraniol (20.6%), citronellol (16.3%), and phenylethyl acetate (7.1%) and that way not very different from Rosa rugosa. „The presence of myrcene (6.6%) accounts for a more balsamic, resinous smell.“
[Flament, I., C. Debonneville, and A. Furrer. „Volatile constituents of roses: characterization of cultivars based on the headspace analysis of living flower emissions.“ chapter in: Volatile compounds from Flowers, Teranishi, R.;Buttery, R. G.;Sugisawa, H. Bioactive volatile compounds from plants. (Book) 1993, 269-281]
Moss roses are old garden roses which flower pedicel and calyx are covered with a green to brown mossy growth. Historically, the first moss roses to be obtained were not sported from R. × centifolia (cabbage rose).
„Chemical analysis of the scent of R. × centifolia ‘muscosa’ and R. × damascena ‘Quatre Saisons Blanc Mousseux’ revealed similar composition of VOCs in the petals and some slight differences in the sepals… In petals of R. × centifolia ‘muscosa’, benzenoids (mostly 2-phenylethanol) made up nearly 60 % of the volatile compounds, as in R. × damascena ‘Quatre Saisons Blanc Mousseux’. Other chemicals were geraniol, nerol, citronellol and their derivatives. Fatty acid derivatives (mostly nonadecane) were also present in both cultivars. In sepals, a noticeable difference was the presence of some specific sesquiterpenes in R. × centifolia ‘muscosa’ (β-farnesene, for example).“
In Rosa × centifolia ‘muscosa’, the mossy leaves and sepals also had the VOC composition of its parent except that fatty acid derivatives (cis-3-hexenol, trans-2-hexenal, trans-2-hexenol and hexanal) were replaced by an increased quantity of monoterpenes, especially myrcene.
[Caissard, Jean-Claude, et al. „Chemical and histochemical analysis of ‘Quatre Saisons Blanc Mousseux’, a moss rose of the Rosa× damascena group.“ Annals of botany 97.2 (2005): 231-238] https://academic.oup.com/aob/article/97/2/231/205860/Chemical-and-Histochem
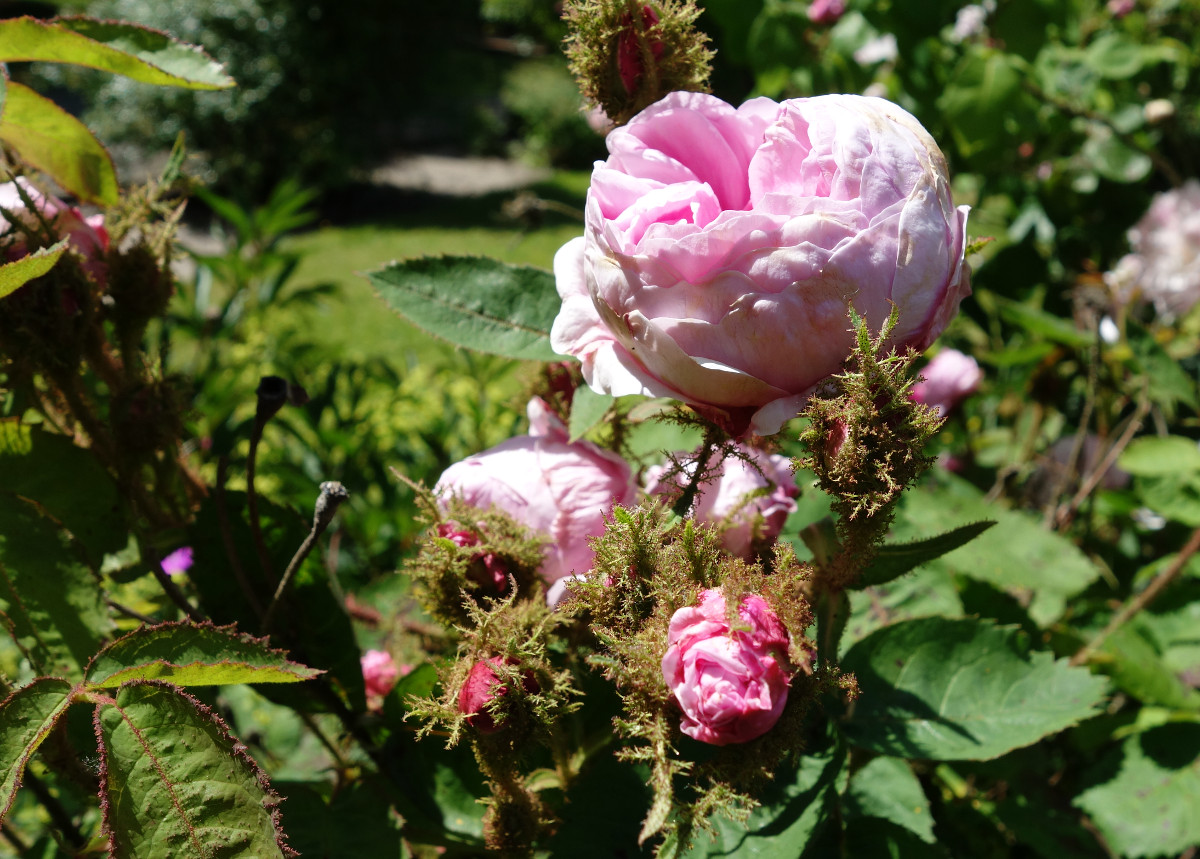

Rosa × centifolia ‚Muscosa‘, CC BY-SA 3.0, Author: Andreas Kraska