Petunia × hybrida (Hook.) Vilm. syn. Petunia × atkinsiana (Sweet) D. Don ex W. H. Baxter - Solanaceae - Petunia, Garten-Petunie
„Petunia × atkinsiana plants were originally produced by hybridisation between P. axillaris (the large white or night-scented petunia) and P. integrifolia (the violet-flowered petunia) and other members of its complex, including Petunia inflata. P. axillaris bears night-fragrant, buff-white blossoms with long, thin tubes and somewhat flattened openings. The scent molecules emitted by the hybrids are generally similar to those from P. axillaris.“ wikipedia
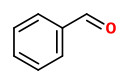
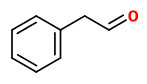
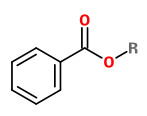
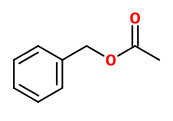
Major volatiles detected in the floral headspace of Petunia hybrida W115 were benzenoids like benzaldehyde, phenylacetaldehyde, methylbenzoate, phenylethylalcohol, isoeugenol, benzylbenzoate, aliphatic aldehydes like decanal and dodecanal, sesquitepenes like germacrene-D and cdina-3,9-diene, and fatty acid-derived aldehydes like 2-hexenal and 3-hexenal.
[Verdonk, Julian C., et al. „Regulation of floral scent production in petunia revealed by targeted metabolomics.“ Phytochemistry 62.6 (2003): 997-1008]
Main compounds emitted from P. axillaris parodii petals and collected by a headspace sampling system
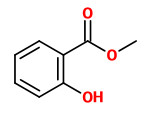
were benzaldehyde and methyl benzoate, followed by benzyl alcohol, benzyl acetate, methyl salicylate, benzyl benzoate, and benzyl salicylate.
[Koeduka, Takao, et al. „The lack of floral synthesis and emission of isoeugenol in Petunia axillaris subsp. parodii is due to a mutation in the isoeugenol synthase gene.“ The Plant Journal 58.6 (2009): 961-969]
„An established model, Petunia×hybrida cv ‘Mitchell Diploid’ (MD) has been used in numerous studies related to floral volatile synthesis. MD has large white flowers that produce copious amounts of floral volatile compounds. Volatile benzenoids and phenylpropanoids dominate the mixture of volatile compounds emitted by the MD flower.“
[Colquhoun, Thomas A., et al. „PhMYB4 fine-tunes the floral volatile signature of Petunia× hybrida through PhC4H.“ Journal of experimental botany 62.3 (2011): 1133-1143]
„Petunia × hybrida cv ‘Mitchell Diploid’ floral volatile benzenoid/phenylpropanoid (FVBP) biosynthesis ultimately produces floral volatiles derived sequentially from phenylalanine, cinnamic acid, and p-coumaric acid… The initial enzymatic sequence of the phenylpropanoid pathway consists of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), and 4-coumaric acid CoA ligase (4CL)…“
White Petunia
CC BY-SA 3.0, derivative work: Julien Demade Wikimedia Commons