Monarda didyma L. - Lamiaceae - scarlet bee balm, Oswego tea, bergamot, Scharlach-Monarde, Scharlach-Indianernessel, Goldmelisse
Perennial herb, up to 1.50m tall, native to eastern Northern America, cultivated as ornamental; leaves ovate-lanceolate, unequally serrate; verticillasters in terminal capitula to 6cm in diam., bracts short petiolate, leaflike, red; flowers scarlet.
„Its odor is considered similar to that of the bergamot orange (the source of bergamot oil used to flavor Earl Grey tea)… Beebalm has a long history of use as a medicinal plant by many Native Americans, including the Blackfeet. The Blackfeet Indians recognized this plant's strong antiseptic action, and used poultices of the plant for skin infections and minor wounds. An herbal tea made from the plant was also used to treat mouth and throat infections caused by dental caries and gingivitis. Beebalm is the natural source of the antiseptic thymol, the primary active ingredient in modern commercial mouthwash formulas. The Winnebago used an herbal tea made from beebalm as a general stimulant. It was also used as a carminative herb by Native Americans to treat excessive flatulence.“
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monarda_didyma
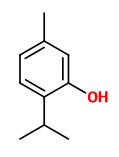
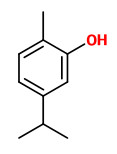
„M.didyma var.80-1A oil was dominated by linalool (55.38%), geraniol (20.71%), and para-myrcene (8.15%). The dominant components of the M. didyma oil were thymol (41.17%), γ-terpinene (15.88%), carvacrol (15.20%), and para-myrcene (12.58%).“
[Variable inhibitory activities of essential oils of three Monarda species on the growth of Botrytis cinerea., Adebayo, O., Bélanger, A., Khanizadeh, S., Canadian Journal of Plant Science, Vol.93(6), 2013, 987-995]
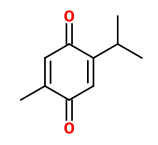
The essential oils of M.didyma obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction contained thymoquinone (36.0%), thymol (16.7%), methyl thymol (7.8%), 1-octen-3-ol (6.5%) , and α-terpinene (3.0%) as main components.
[Effect of the volatile scondary metabolites of Monarda didyma L., Lamium album L. and myrrhis odorata L. plants against micromycetes of indoor environments of animals., Mickienė, R., Bakutis, B., Maruška, A., Ragažinskienė, O., & Kaškonienė, V., Veterinarija ir Zootechnika, 68(90), 2014] http://vetzoo.lva.lt/data/vols/2014/68/pdf/mickiene.pdf
The volatile oil extracted from dry aerial parts of scarlet bee balm with supercritical CO2 gave thymoquinone 0.6mg/g.
[Supercritical CO 2 extraction of volatile thymoquinone from Monarda didyma and M. fistulosa herbs., Sovova, H., Sajfrtova, M., Topiar, M., The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2015]
Hydrodistillation of thymoquinone from wild bergamot (Monarda didyma) with supercritical CO2 leads to substantial loss of this compound. Extraction with hexane yield thymoquinone (0.7mg/g, extract thymoquinone concentration 2.6%), while supercritical CO2 extraction was 0.6mg/g with high thymoquinone concentration in the extract (5.2% w/w).
[Sovova, Helena, Marie Sajfrtova, and Martin Topiar. „Supercritical CO2 extraction of volatile thymoquinone from Monarda didyma and M. fistulosa herbs.“ The Journal of Supercritical Fluids 105 (2015): 29-34]
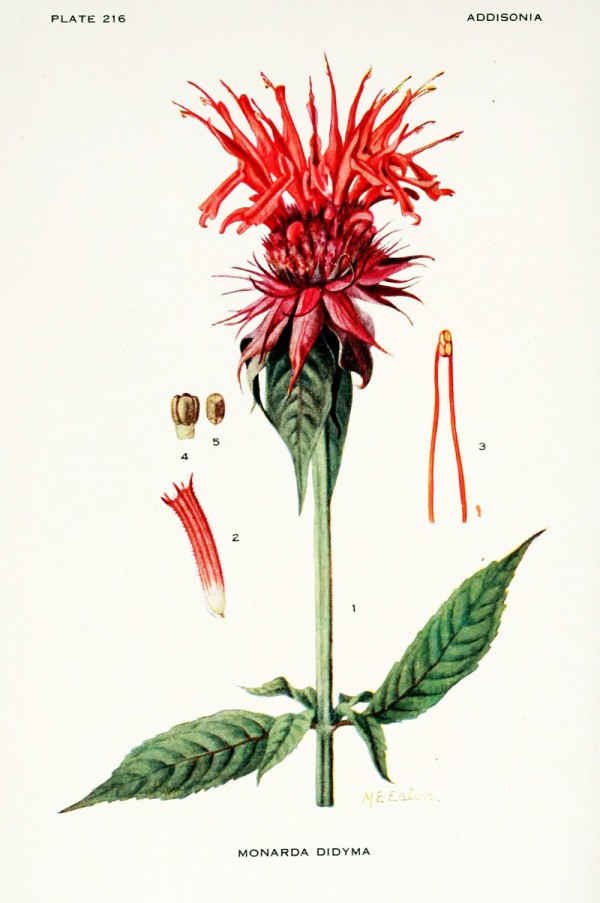

Addisonia, vol.6 t.216 (1921) [M.E.Eaton]
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=677742
Monarda didyma
© Rolf Marschner (2006),
www.botanische-spaziergaenge.at