Eutrema japonicum (Miq.) Koidz. - syn. Wasabia japonica (Miq.) Matsum.; Eutrema wasabi Maxim.; Cochlearia wasabi Siebold - Brassicaceae
Japanese horseradish, Japanischer Meerrettich, Wasabi
Perennial herb, up to 60cm tall, native to Japan, Korea, Sakhalin, cultivated in Japan, Korea and Taiwan for its edible rhizomes (source of the pungent condiment, wasabi).
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=241000220
„Its stem is used as a condiment and has an extremely strong flavor. Its hotness is more akin to that of a hot mustard than that of the capsaicin in a chili pepper, producing vapours that stimulate the nasal passages more than the tongue.“ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wasabi
Fresh wasabi paste made by crushing the root develops a characteristically fresh greenish flavor clearly different from the flavors of pastes from the other glucosinolates containing plants. LC/GC/MS/1H-NMR showed 6-methylthiohexyl isothiocyanate (2mg/kg), 7-methylthioheptyl isothiocyanate and 8-methylthiooctyl isothiocyanate to be the characteristic greenish wasabi flavor components.
[ω-Methylthioalkyl isothiocyanates in Wasabi. Agricultural and biological chemistry, INA, Kazuo, et al., Vol.53, 1989, 537-538]
The rhizome contains most of the flavour and is the part most widely used, although both the leaves and petioles contain some of the flavour. Wasabi myrosinase liberates a mixture of isothiocyanates from precursor molecules, giving wasabi its distinctive flavour.
[Flavour and pharmaceutical properties of the volatile sulphur compounds of Wasabi (Wasabia japonica). Depree, J.A., Howard, T.M., Savage, G.P., Food research international, 31(5), 1998, 329-337]
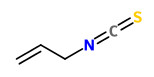
The main volatile components of E.wasabi grown in Yunnan were identified as 1,6-hexane diisothiocyanate (30.7%) and allyl isothiocyanate (17.1%) with GC-MS.
[Study on Volatile Components Of Yunnan Eutrema Wasabi Maxim., LU, Li-he, et al. Yunnan Chemical Technology, Vol.5, 2011, 4]
Total content of isothiocyanates of Japanese horseradish rhizome grown in New Zealand was 2067mg/kg fresh weight, with allyl isothiocyanate (AITC, 1937 mg/kg) as the main component. Minor components present were 3-butenyl isothiocyanate (43 mg/kg), 4-pentenyl isothiocyanate (47 mg/kg), sec-butyl isothiocyanate (18 mg/kg), isopropyl isothiocyanate (12 mg/kg) and 5-hexenyl isothiocyanate (7 mg/kg).
[Comparison of flavour compounds in wasabi and horseradish., Sultana, T., Savage, G. P., McNeil, D. L., Porter, N. G., Clark, B., Journal of Food Agriculture & Environment, Vol.1(2), 2003, 117-121] http://www.coppersfolly.co.nz/v1/research/comparison2.pdf
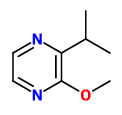
„Freshly grated wasabi aroma was investigated by aroma extract dilution analysis. At the highest flavor dilution factors of 1024 and 256, ten odorants were detected as odor-active compounds: allyl isothiocyanate, (Z)-1,5-octadien-3-one, 4-pentenyl isothiocyanate, 5-hexenyl isothiocyanate, 3-methyl-2-butene-1-thiol, 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine, 3-methyl-2,4-nonanedione, cis-3-methyl-4-decanolide, 6-(methylthio)hexyl isothiocyanate, and vanillin. To determine the absolute configuration of cis-3-methyl-4-decanolide in wasabi, the stereoisomers of 3-methyl-4-decanolide were synthesized from optically active γ-decalactone. Finally, the absolute configuration of cis-3-methyl-4-decanolide in wasabi was determined as (3R,4R)-3-methyl-4-decanolide by chiral GC-MS. Sensory analysis revealed that the (3R,4R)-3-methyl-4-decanolide constitutes an essential part of fresh wasabi aroma.“
[Nakanishi, Akira, et al. „(3R,4R)-3-Methyl-4-decanolide, a Novel Lactone Contributing to Fresh Wasabi (Wasabia japonica) Aroma.“ Importance of Chirality to Flavor Compounds. American Chemical Society, 2015. 99-108]
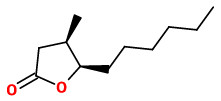
Synthesis of both enantiomers of cis-3-methyl-4-decanolide showed that the (3R,4R) isomer has a lactonic-fatty top note and a lactonic-green middle note.
[Masuzawa, Yoko, Shigeyuki Tamogami, and Takeshi Kitahara. „Synthesis of both enantiomers of cis-methyl-4-decanolide, a key component for the scent of African orchids.“ Natural Product Letters 13.4 (1999): 239-246]
„The main bioactive compound of wasabi is 6-MSITC (6 methylsulfinyl hexyl isothiocyanate), which has anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory functions. Anti-oxidants and anti-inflammatories have an important role in cognitive health. Therefore, 6-MSITC is expected to have positive effects on cognitive function. Previous studies showed the beneficial effects on cognitive functions in middle-aged adults. However, it is unclear that 6-MSITC has a positive effect on cognitive functions in healthy older adults aged 60 years and over. Here, we investigated whether 12 weeks’ 6-MSITC intervention enhances cognitive performance in older adults using a double-blinded randomized controlled trial (RCT). Methods: Seventy-two older adults were randomly assigned to 6-MSITC or placebo groups. Participants were asked to take a supplement (6-MSITC or a placebo) for 12 weeks… We found two main findings. First, the 6-MSITC intervention improved working memory capacity as measured by DS-B compared to the placebo group. Second, the 6-MSITC intervention improved episodic memory performances as measured by LM and FSM. … This study firstly demonstrates scientific evidence that 6-MSITC may enhance working memory and episodic memory in older adults. We discuss the potential mechanism for improving cognitive functions after 6-MSITC intake.“
[Nouchi, Rui, et al. „Benefits of Wasabi Supplements with 6-MSITC (6-Methylsulfinyl Hexyl Isothiocyanate) on Memory Functioning in Healthy Adults Aged 60 Years and Older: Evidence from a Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial.“ Nutrients 15.21 (2023): 4608]
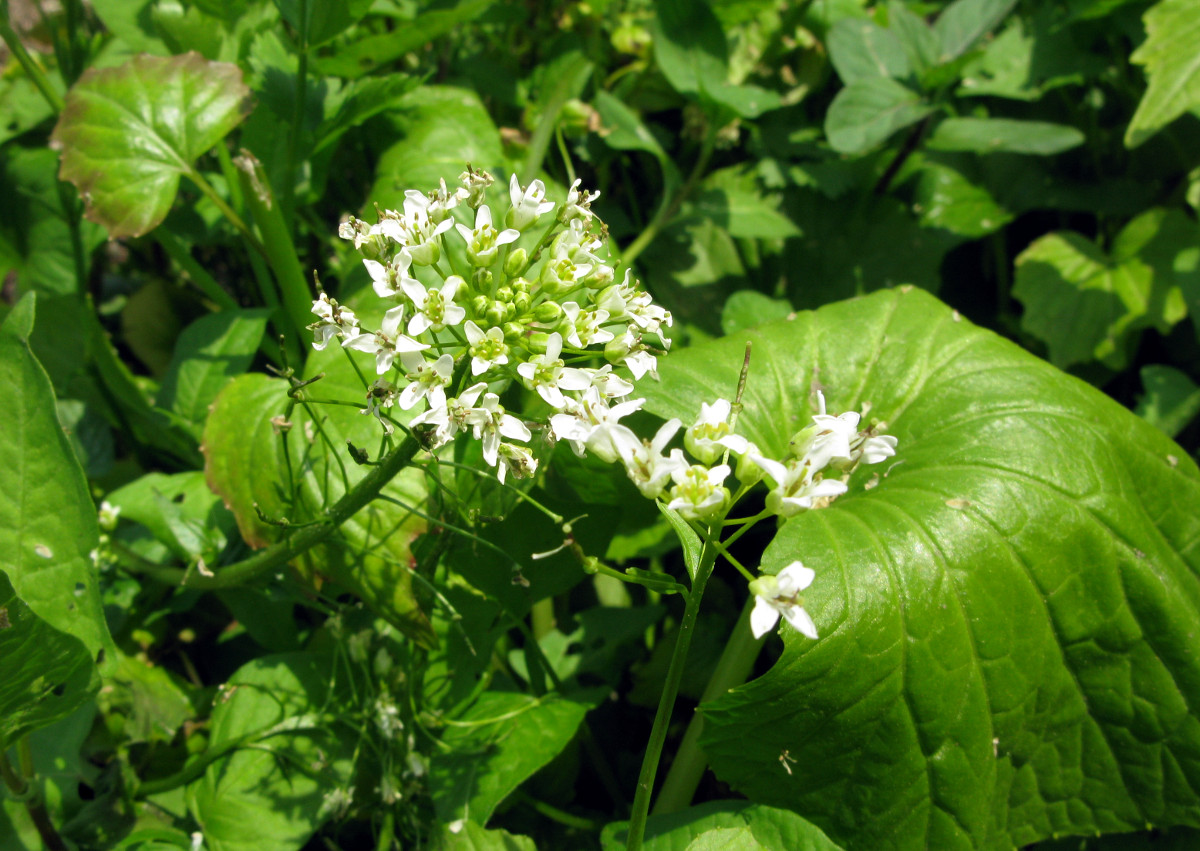

Wasabia japonica, Aizu area, Fukushima pref., Japan
Author: Qwert1234CC BY-SA 3.0 Wikimedia Commons