Eupatorium cannabinum L. - Asteraceae - hemp agrimony, Echter Wasserdost, Gewöhnlicher Wasserdost, Kunigundenkraut
Perennial herb, 0.50-1.50m high, native to Europe, North Africa, Central Asia, naturalized elsewhere; leaves opposite, palmate; flower-heads small (2-5mm), petals pink to red or nearly white.
„Traditionally, E.cannabinum is used to treat rheumatic diseases, fever and flu-like infections. The immunostimulating effect is primarily due to the content of immunostimulatory polysaccharides.“
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gew%C3%B6hnlicher_Wasserdost
„From the alkaline aqueous extract of the herbal part of Eupatorium cannabinum and Eupatorium perfoliatum two homogeneous polysaccharides (PI and PII) have been isolated by ethanol precipitation and fractionation on DEAE Sepharose CL-6B and Sephacryl S-400 columns… The polysaccharides show a phagocytosis enhancing effect as determined in three immunological test systems (carbon clearance, granulocyte- and chemiluminescence test).“
[Immunologically active polysaccharides of Eupatorium cannabinum and Eupatorium perfoliatum., Vollmar, A., Schäfer, W., Wagner, H., Phytochemistry, Vol.25(2), 1986, 377-381]
„Compounds identified in aerial parts of E.cannabinum in this way are four echinatine isomers, like lycopsamine and intermedine, and a number of their β-acetyl, β-angelyl/tiglyl and β-(iso)valeryl esters. PAs without a substituent at C-7 were tentatively identified as supinine and amabiline. In addition to a number of these alkaloids, some β-(iso)butyryl, β-angelyl/tiglyl, and β-(iso)valeryl esters of supinine or amabiline were detected in subterranean parts of the plant.“
[Investigation into the Presence of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Eupatorium cannabinum by Means of Positive and Negative Ion Chemical Ionization GC-MS., Hendriks, H., Balraadjsing, W., Huizing, H.J., Bruins, A.P., Planta medica, Vol.53(5), 1987, 456-461]
„The essential oil from aerial parts of Eupatorium cannabinum L. subsp. cannabinum L. (Asteraceae) was obtained by hydrodistillation. The oil content was 0.37% (v/w), on a dry weight basis. The oil composition was analyzed by GC and GC/MS. Fifty-nine compounds were identified accounting for 94.1% of the oil. Germacrene D (33.5%) was the most abundant component with appreciable amounts of α-farnesene (12.9%) and δ-2-carene (6.5%). Between the oxygen containing components elemol (2.8%) and α-cadinol (2.7%) were the most abundant. The oil shows an interesting antibacterial activity, mostly against Gram + bacteria.“
[Eupatorium cannabinum L. ssp. cannabinum (Asteraceae) essential oil: chemical composition and antibacterial activity., Senatore, F., De Fusco, R., Napolitano, F., Journal of Essential Oil Research, Vol.13(6), 2001, 463-466]
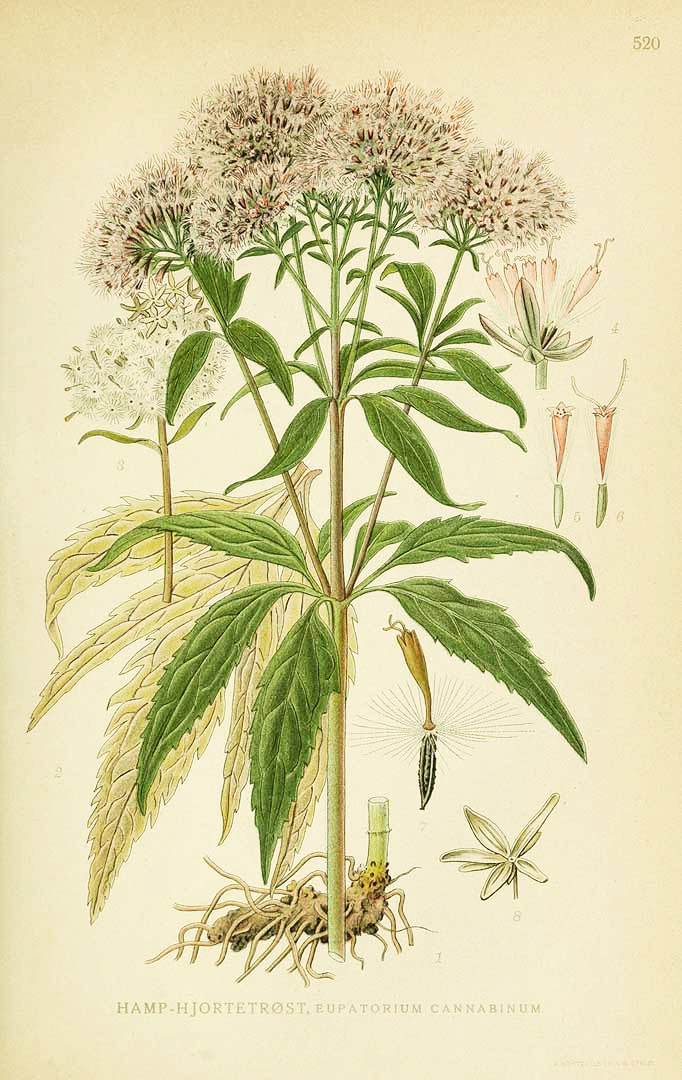
Lindman, C.A.M., Bilder ur Nordens Flora, vol. 3: t. 520 (1922-1926)
http://www.plantillustrations.org/species.php?id_species=417794
