Eucalyptus olida L.A.S. Johnson & K.D. Hill - Myrtaceae - strawberry gum
Tree, up to 30m high, endemic to a restricted area of New South Wales, Australia; bark fibrous, flaky; young leaves blueish green, elliptic; adult leaves alternate, dull green, lanceolate to narrow lanceolate; flowers white; fruit a woody, bell-shaped capsule. „Eucalyptus olida belongs to the blue-leaved ashes and has the peppermint-type bark of E. andrewsii and E. consideniana, with fruit more like E. andrewsii subsp. andrewsii, from which it differs in the methyl cinnamate oil of the leaves, that normally can be detected as a unpleasant odour when the fresh leaves are crushed.“
Eucalyptus olida. Euclid: Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research. Retrieved 17 October 2022.
„Steam distillation of the leaf of a New England blackbutt, Eucalyptus sp. nov. aff. campanulata gave an essential oil rich in E-methyl cinnamate with trans-β-ocimene as minor component and methyl 2-methyl butyrate, α-pinene, cis-β-ocimene, Z-methyl cinnamate and α, β and γ-eudesmol as trace constitutents. Interpopulational studies showed a 2-6 percent range in oil yield with 94-99% E-methyl cinnamate content.“
[Curtis, Alison, Ian A. Southwell, and Ian A. Stiff. „Eucalyptus, a new source of E-methyl cinnamate.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 2.3 (1990): 105-110]
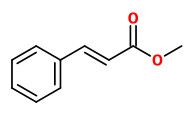 (E)-methyl cinnamate (sweet balsam fruity)
(E)-methyl cinnamate (sweet balsam fruity)
Extracts (petrol ether) of Eucalyptus olida leaves and stems from 3-5 year old trees in a trial planting contained very high levels (>91% of oil yield) of methyl cinnamate, but some trees had low (0%) or variable levels (0-21%).
[Smale, Peter E., et al. „Essential oil of Eucalyptus olida L. Johnson et K. Hill 1: Variability of yield and composition in foliage from a seedling population.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 12.5 (2000): 569-574]
„(E)-methyl cinnamate, accounted for 99.4% of the essential oils of E. oilda, although 19 compounds were identified.“
[Gilles, Martin, et al. „Chemical composition and antimicrobial properties of essential oils of three Australian Eucalyptus species.“ Food Chemistry 119.2 (2010): 731-737]
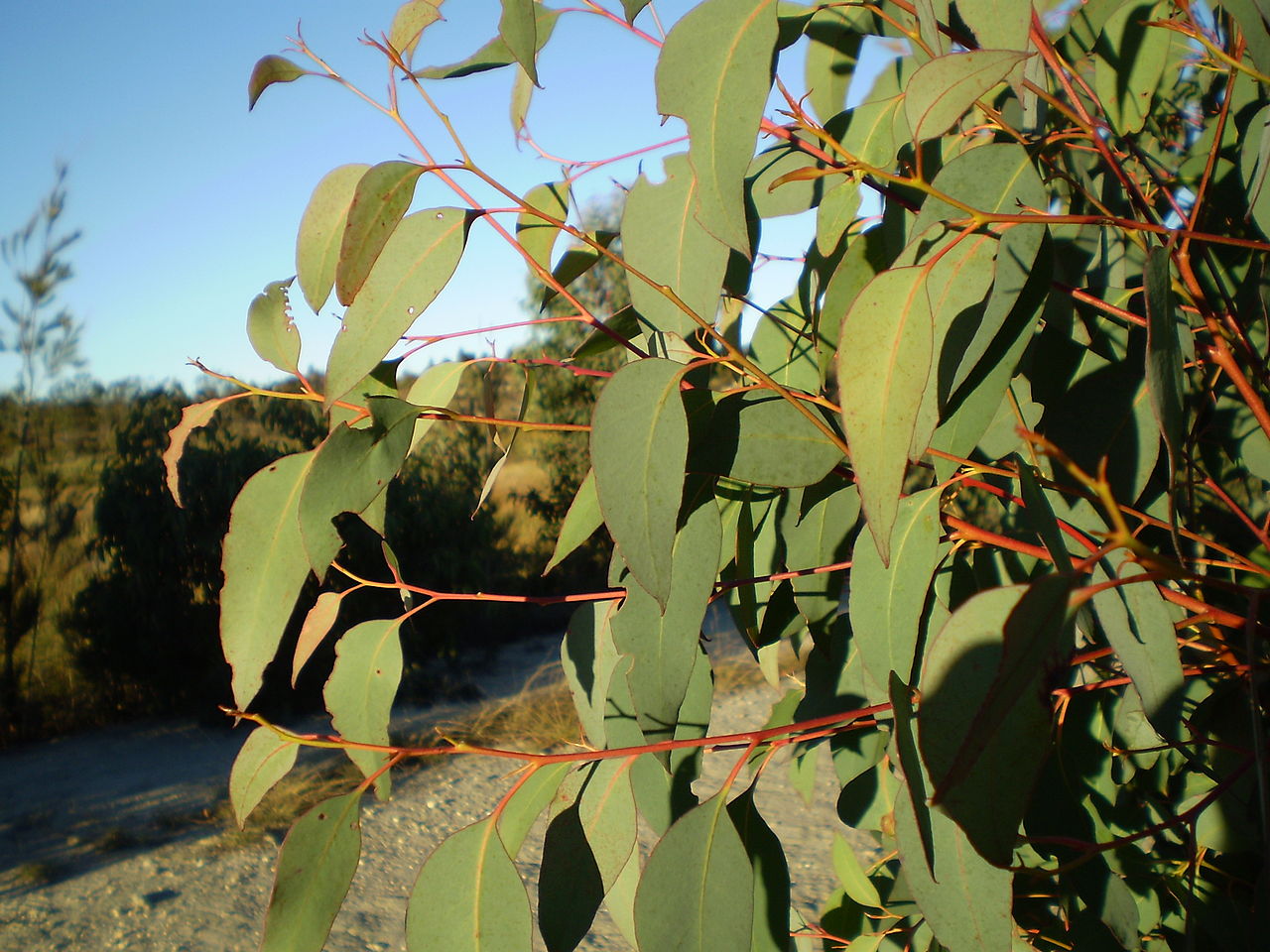

Eucalyptus olida, strawberry gum, juvenile foliage; John Moss (2008) wikimedia commons, © Public Domain
