Benutzer-Werkzeuge
Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Iridaceae - saffron, saffron crocus, Safran, Echter Safran, Gewürzsafran
Perennial without above-ground stem, unknown as a wild plant; leaves 2-4, linear, with a white midrib, 8-15cm long, appearing in autumn with the lilac-purple flowers; anthers yellow, filaments purple; style red, branched, up to 3cm long; fruit 3-celled capsule.
„Cultivated in the main Kashmir valley. Being a triploid it is sterile and propagated by vegetative means only. Known only under cultivation; Saffron, obtained from long red style branches and stigmas are in great demand for eastern culinary preparations and in medicine. It is rich in vitamin B2.“ http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=5&taxon_id=200028148
The carotenoid crocin is primarily responsible for the color of saffron.
„Safranal, the main component of Crocus sativus essential oil, is thought to be the main cause of saffron unique odor… Beside its exclusive color, saffron presents a particular taste which is originates from its picrocrocin content. Safranal (2,6,6-trimethyl-1,3-cyclohexadien-1-carboxaldehyde) is a cyclical terpenic aldehyde produced from picrocrocin. Picrocrocin, discovered by Kajser (1884), cracks down following acids and alkali conditions, resulting in a molecule of water and an aglycon which in turn, loses a water molecule and finally turns to safranal. Kuhn and Winterstein (1933), who obtained safranal through picrocrocin hydrolyzation for the first time, named this chemical as Safranal.“
[Safranal: From an Aromatic Natural Product to a Rewarding Pharmacological Agent. Ramin Rezaee1 and Hossein Hosseinzadeh, Iran J Basic Med Sci. Jan 2013; 16(1), 2013, 12–26]
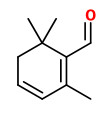
4-Hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde is a precursor of safranal and may be obtained by mild extraction methods like ultrasound-assisted extraction in amounts of 0.4mg/g saffron (safranal: 6mg/g).
[Qualitative determination of volatile compounds and quantitative evaluation of safranal and 4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde (HTCC) in Greek saffron. Kanakis, C. D., Daferera, D. J., Tarantilis, P. A., & Polissiou, M. G., Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, Vol.52(14), 2004, 4515-4521]
Aroma extract dilution analysis (AEDA) was used for the determination of aroma-active compounds of Iranian saffron obtained by solvent-assisted flavour evaporation (SAFE). „According to sensory analysis, the
aromatic extract obtained by SAFE was the most representative of saffron odour…. A total of nine aroma-active compounds were detected in the aromatic extract. On the basis of the flavour dilution (FD) factor, the most powerful aroma active compounds were safranal (FD = 512), 4-ketoisophorone (FD = 256) and dihydrooxophorone (FD = 128).“
[GC-MS-olfactometric characterization of the most aroma-active components in a representative aromatic extract from Iranian saffron (Crocus sativus L.)., Amanpour, A., Sonmezdag, A.S., Kelebek, H., Selli, S., Food chemistry, 182, 2015, 251-256]