Couroupita guianensis Aubl. - Lecythidaceae - cannonball tree, Kanonenkugelbaum
Deciduous tree; bark smooth; leaves in clusters at the ends of branches, entire, oblong, obovate, elliptic or broadly lanceolate, 10-16cm long, 4-6cm broad; flowers in racemes 40-80cm long, fragrant, 8-15cm across, petals fleshy, yellow and red; fruit brown, globular, up to 25cm in diameter, hard (woody) outside, the pulp inside white, cheese-like, with unpleasant smell.
„It is native to the tropical forests of Central and South America, and it is cultivated in many other tropical areas throughout the world because of its beautiful, fragrant flowers and large, interesting fruits.“ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Couroupita_guianensis
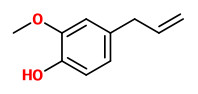
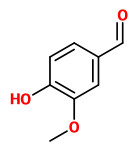
The flowers emit their intensily sweet scent especially in the night. Main volatile constituents of a solvent extract were eugenol (41.6%), linalool (14.9%), (E,E)-farnesol (10.3%), nerol (9.8%), geraniol (5.4%), phenylethanol (3.2%), and benzylalcohol (2.0%). Minor components were e.g. 1-octen-3-ol (0.5%), diethyl oxalate (0.5%), diethyl succinate (0.3%), ethyl salicylate (0.4%), ethyl palmitate (1.4%), (Z,E)-farnesol (0.9%), and vanillin (0.3%).
[Wong, K. C., and D. Y. Tie. „Volatile constituents of Couroupita guianensis Aubl. flowers.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 7.2 (1995): 225-227], see also [Dragoco Report 1997, 2, 63-71]
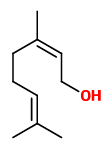
„The major components identified in the flowers of C. guianensis were linalool (21.5%), eugenol (18.9%) and (E,E)-farnesol (16.1%).“
[Andrade, Eloisa Helena A., Maria das Graças B. Zoghbi, and José Guilherme S. Maia. „The volatiles from flowers of Couroupita guianensis Aubl., Lecythis usitata Miers. var. paraensis (Ducke) R. Kunth. and Eschweilera coriacea (AP DC.) Mori (Lecythidaceae).“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 12.2 (2000): 163-166]
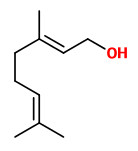
Main volatile components of the flowers, analyzed using HS-SPME and GC-MS, were eugenol (18.9%), nerol (13.5%), (E,E) farnesol (12.9%), (E,E)-farnesyl acetate (6.7%), (E)-ocimene (6.0%), nootkatone (4.6%), geraniol (2.9%), lavandulyl acetate (2.7%), cedr-8-en-13-ol (2.6%), and (E,Z)-farnesyl acetate (2.4%).
„Linalool was the major chemical (21.5% and 14.9%) in solvent extract and micro-simultaneous extract, respectively, but appeared in negligible quantity (0.16%) in headspace analysis.“
[Khan, Arpita Mandal, K. S. Shivashankara, and T. K. Roy. „Determining composition of volatiles in Couroupita guianensis Aubl. through headspace-solid phase micro-extraction (HS-SPME).“ Journal of Horticultural Sciences 9.2 (2014): 161-165]
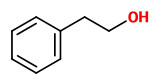
Main components of the steam-distilled essential oil of the flowers were eugenol (46.2%), 2-phenylethanol (34.8%), (E,E)-farnesol (5.5%), nerol (3.9%), geraniol (3.2%), and benzyl alcohol (1.7%).
[della Cuna, Francesco Saverio Robustelli, et al. „Chemical composition and Antioxidant activity of essential oil from flowers of Couroupita guianensis Aubl. from El Salvador.“, Open J. Chem. 2020, 3(1), 1-6; doi:10.30538/psrp-ojc2020.0016]
https://pisrt.org/psrpress/j/ojc/2020/1/1/chemical-composition-and-antioxidant-activity-of-essential-oil-from-flowers-of-couroupita-guianensis-aubl.-from-el-salvador.pdf

Couroupita guianensis flowers and fruits
CC BY-SA 3.0, Author: Mokkie Wikimedia Commons