Boswellia papyrifera (Delile ex Caill.) Hochst. - syn.Amyris papyrifera Delile ex Caill. - Burseraceae
Ethiopian frankincense, Ethiopischer Weihrauchbaum
Boswellia papyrifera is a drought-resistant tree of Central and eastern Africa and a source of frankincense.
„… deciduous tree which can be as tall as 12 m, with a rounded crown and a straight regular bole. The bark is whitish to pale brown, peeling off in large flakes; slash red-brown and exuding a fragrant resin. The bark contains schizogenous olea-gum-resin pockets (Verghese 1988). Leaves are large, compound, arranged on long stalks with 11 to 29 leaflets which are narrowly ovate to oblong, waved or toothed along the margin. B. papyrifera is a monocious species with sweet scented flowers which are white to pink, arranged on long red flower stalks, in loose panicles at the end of branches. Fruits are obtetrahedral, which are red capsules about 2 cm long, usually containing three tapered seeds.“ fao.org
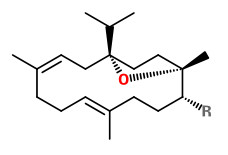
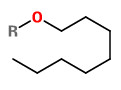
„The chemical composition of B.papyrifera is markedly different from that of other Boswellia…“ Main volatile compounds of B.payprifera detected by headspace SPME-GC/MS were n-octyl acetate (64.6%), octanol (13.9%), cembrene A (1.7%) and incensole (1.0%).
[A chemical investigation by headspace SPME and GC-MS of volatile and semi-volatile terpenes in various olibanum samples. Hamm, S., Bleton, J., Connan, J., & Tchapla, A., Phytochemistry, Vol.66(12), 2005, 1499-1514]
„Both n-octanol and n-octyl acetate, along with the diterpenic components incensole and incensole acetate, were the characteristic compounds of B. papyrifera oleogum resin oil.“
[Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Some Oleogum Resin Essential Oils from Boswellia SPP. (Burseraceae), Lorenzo Camarda, Talya Dayton, Vita Di Stefano, Rosa Pitonzo, Domenico Schillaci, Annali di Chimica, Vol.97(9), 2007, 837-844]
The orange colored neutral fraction of the diethyl ether extract from B.papyrifeira resin contained incensole (18.8-24.9%) and incensole acetate (14.0-18.5%).
[Paul, Michael, and Johann Jauch. „Efficient preparation of incensole and incensole acetate, and quantification of these bioactive diterpenes in Boswellia papyrifera by a RP-DAD-HPLC method.“ Natural product communications 7.3 (2012): 1934578×1200700303] PDF
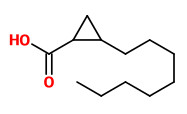
The (1S,2S)-(+)-trans- and (1S,2R)-(+)-cis-2-octylcyclopropyl-1-carboxylic acids (olibanic acids) „…were also
present in the octyl-acetate-type EO (presumably B. papyrifera).“
These acids provide the very characteristic old churchlike endnote of the frankincense odor.
[Cerutti‐Delasalle, C., Mehiri, M., Cagliero, C., Rubiolo, P., Bicchi, C., Meierhenrich, U. J., & Baldovini, N. (2016). The (+)‐cis‐and (+)‐trans‐Olibanic Acids: Key Odorants of Frankincense. Angewandte Chemie, 128(44), 13923-13927]

Richard, A., Tentamen florae Abyssinicae, Atlas, t.33 (1851) [A.C.Vauthier]
plantgenera.org
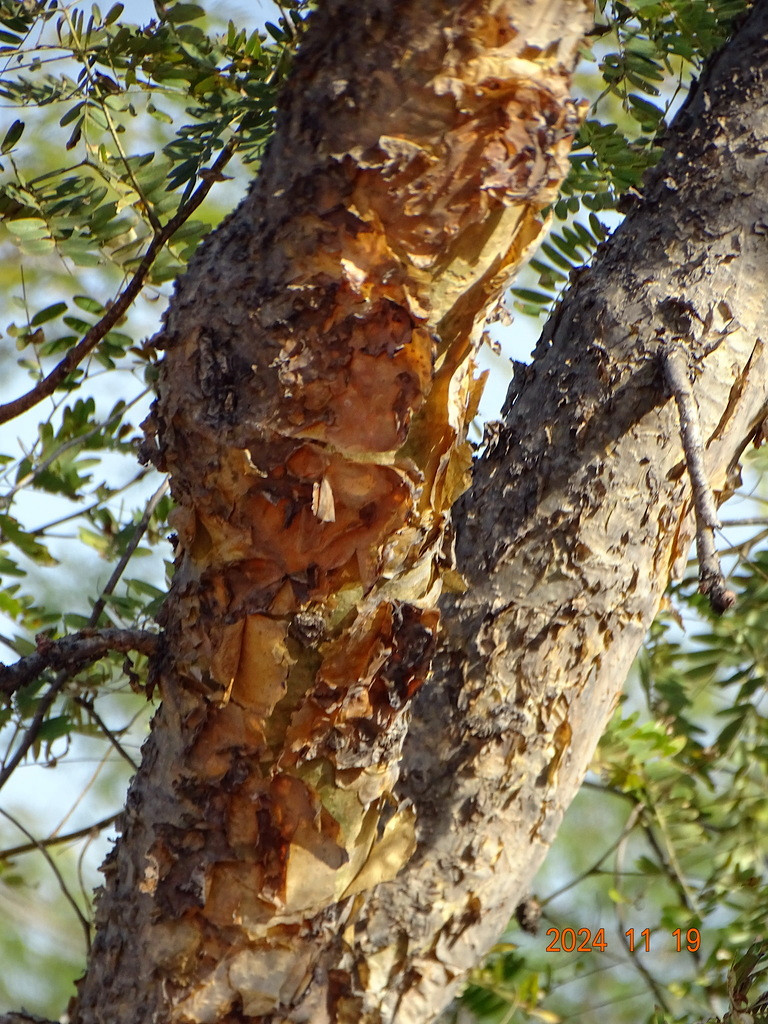

Boswellia papyrifera, Birao, Central African Republic (2024) © thierry_aebischer_chinko CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org