Asarum canadense L. - Aristolochiaceae - American wild ginger, Canada snakeroot, Kanadische Haselwurz
Prostrate evergreen perennial, up to 10cm high, native to eastern North America; slender rhizome with the smell of ginger; stems short, developing in spring, each branch with one leave; leaves dark green, reniform (kidney-shaped), downy at both sides, 5-20cm across; flowers on short stalkes near ground, solitary, dark purple-brown, campanulate; fruit a coriaceous, 6-celled capsule.
„Flowers are quite attractive on close inspection, but bloom singly on or near the ground and are usually hidden from view by the foliage. Although not related to culinary ginger (Zingiber officinale), the roots of this plant produce a scent that is reminiscent thereof. Fresh or dried roots were used by early Americans as a ginger substitute, but the plant is not normally used today for culinary purposes.“ http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=b460
„Native Americans used Asarum canadense medicinally to treat flux, poor digestion, swollen breasts, coughs and colds, typhus and scarlet fever, nerves, sore throats, cramps, heaves, earaches, headaches, convulsions, asthma, tuberculosis, urinary disorders, and venereal disease; as a stimulant, a seasoning, and a charm; and to strengthen other herbal concoctions and heighten appetite (D.E. Moerman 1986).“
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=233500168
„A pentane extract from the rhizomes of Asarum canadense was separated first by means of steam distillation, and then by column and gas chromatography. From the steam-volatile oil the following constituents were isolated (percentages are shown in parentheses): methyleugenol (44.5), linalyl acetate (41.1), geraniol (7.4), linalool (5.3), limonene (0.8), α-terpineol (0.4), bornyl acetate (0.3), aristolone (0.1), elemicin (0.1), 2,3,4,5-tetramethoxyallylbenzene (0.05), 2,4-dimethoxycinnamaldehyde (0.05), and two unidentified compounds (0.01 each). The steam-nonvolatile residue contained some of the above and also β-sitosterol.“
[Constituents of the rhizome of Asarum canadense., Bauer, L., Bell, C.L., Gearien, J.E., Takeda, H., Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 56(3), 1967, 336-343]
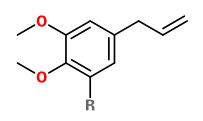 methyl eugenol (R=H) (cinnamon clove) elemicin (R=OCH3) (spicy floral) | 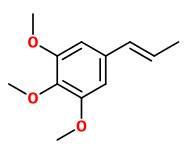 (E)-isoelemicin (spicy floral) |
„The fresh rhizomes and roots of Asarum canadense were steam-distilled to yield oils in 1.30% to 1.96%, respectively. The oils were analyzed by a combination of GC-FID and GC/MS techniques. In the case of the rhizome oil, the total amount of phenyl ethers including methyl eugenol, elemicins, and asaricin was about 58%. In the root oil, (E)-isoelemicin was the major product (20%) accompanied by elemicin (4.9%). From retention indices on both non-polar and polar columns and MS considerations, it may be inferred that methoxy-elemicin and both (E)- and (Z)-methoxy-isoelemicin as well as the new hydroxyl derivatives: hydroxyl-elemicin and (E)- and (Z)-hydroxy-isoelemicins were characterized in the oils.“
[Aromas From Quebec. II. Composition of the Essential Oil of the Rhizomes and Roots of Asarum canadense L., Bélanger, A., Collin, G., Garneau, F.X., Gagnon, H., Pichette, A., Journal of Essential Oil Research, 22(2), 2010, 164-169]
In 2010, the use of all plants belonging to the Asarum species in drugs was banned in Germany by decree of the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM). The cause of this was the detection of aristolochic acid I in homeopathic mother tinctures of Asarum europaeum with approximately 44-128µg/kg, and of Asarum canadense with approximately 127µg/kg.
http://www.bfarm.de/SharedDocs/Downloads/DE/Arzneimittel/Pharmakovigilanz/Risikoinformationen/RisikoBewVerf/a-f/aristolochia_bescheid.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=2
Methyl eugenol was the main component of the rhizomes essential oil (38.5%), followed by linalool (19.4%) and α-terpineol (5.9%). Minor compounds were 1,8-cineole (0.3%), terpinen-4-ol (0.5%), nerol (1.2%), geraniol (3.6%), neryl acetate (1.4%), elemicin (1.1%), methoxyelemicin (0.6%), 5-epi-7-α-eudesmol, and (E)-isoelemicine (1.3%). Methyl eugenol was the main products in the rhizomes essential oil, (E)-isoelemicin was the main product extracted from the roots (ca.20%).
[Chemical composition and stability of the hydrosols obtained during essential oil production. I. The case of Melissa officinalis L. and Asarum canadense L., Garneau, F.X., Collin, G., Gagnon, H., Am. J. Essent. Oils Nat. Prod, 2, 2014, 54-62]
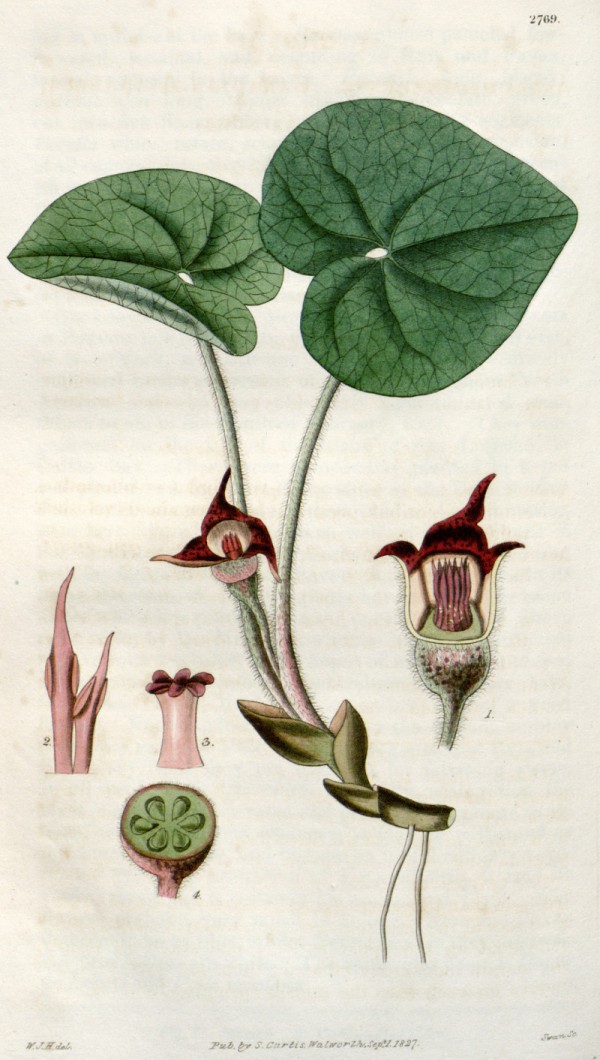

Curtis’s Botanical Magazine, vol.54 [ser.2, vol.1] t.2769 (1827) [W.J.Hooker]
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=95831
Asarum canadense
© Rolf Marschner (2008),
www.botanische-spaziergaenge.at
