Artemisia vulgaris L. - Asteraceae - mugwort, armoise commun (fr.), (Gemeiner) Beifuss
Upright perennial, up to 1,60m high, native to Europe, Asia, naturalized in America; stem red to reddish-brown, panicle-like branched, woody at its base; leaves pinnatisect, with lanceolate tips, dark green and glabrous above, tomentose beneath; upper leaves simple or only three-lobed; panicles of small flowerheads with yellowisch or reddish brown florets.
„Since ancient times, mugwort has been used for numerous medicinal and magical purposes. The main modern use is as an aromatic bitter to treat dyspepsia and lack of appetite… the therapeutic value has not yet been substantiated by modern studies.“
[Medicinal Plants of the World. Ben-Erik Van Wyk and Michael Wink, Pretoria 2004, 57]
The bitter principle of A.vulgaris are sesquiterpene lactones, mainly vulgarin (1.5%, also called judaicin or tauremisin from A.judaica and Artemisia taurica).
[Vulgarin, a Sesquiterpene Lactone from Artemisia vulgaris L., Geissman, T.A., Ellestad, G.A., The Journal of Organic Chemistry, Vol.27(5), 1962, 1855-1859]
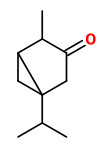
 vulgarin (barrelin, judaicin, tauremisin, CAS 3162-56-9)
vulgarin (barrelin, judaicin, tauremisin, CAS 3162-56-9)
„Artemisia vulgaris was cultivated under subtropical Indo-gangetic plain conditions to determine the differences in the chemical composition of its essential oil produced from plants harvested at different growth periods using a combination of GC and GC/MS. The oil yield ranged from 0.1-0.5%. The leaf oil was found to be rich in 1,8-cineole (2.2-12.2%), α-thujone (0-11.4%), camphor (15.7-23.1%) and isoborneol (9.3-20.9%). The fruit oil contained α-thujone (15.5-16.0%) and artemisia alcohol (16.3-17.7%) as major components, while camphor (38.7%) predominated in the flower oil.“
[Essential oil composition of Artemisia vulgaris harvested at different growth periods under Indo-Gangetic plain conditions. Haider, F., Dwivedi, P.D., Naqvi, A.A., Bagchi, G.D., Journal of Essential Oil Research, Vol.15(6), 2003, 376-378]
 (α + β) thujone | 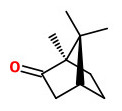 camphor | 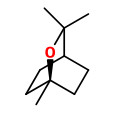 1,8-cineole | 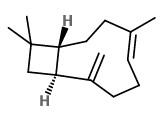 β-caryophyllene |
„The chemical composition of the essential oils of Artemisia vulgaris L. growing in Northern Lithuania has been studied. The wild growing plants were collected in seven localities at the early flowering stage in 2004 and 2005; oils were prepared by hydrodistillation of mugwort overground parts and analyzed by GC/MS. Germacrene D has been found as the first principal component in three oils (10.6-15.1%), in two oils as the second (12.1 and 13.4%) and in one oil as the third (10.3%). trans-Thujone was determined as the first major constituent in one oil (20.2%) and cis-thujone as the second dominant compound in one oil (12.9%). Chrysanthenyl acetate prevailed in one oil (23.6%). 1,8-Cineole was the predominant constituent in two oils (16.7 and 17.6%). Among the other major compounds were sabinene, β-pinene, artemisia ketone, caryophyllene.“
[Chemical composition of essential oils of Artemisia vulgaris L.(mugwort) from North Lithuania. Judžentienė, A., Buzelytė, J., Chemija, vol.17(1), 2006, 12-15]
„Fresh leaves were collected from greenhouse-grown plants and subjected to essential oil analysis by the simultaneous distillation and extraction method. GC-MS results revealed the presence of 88 components and the extracted oil was rich in camphor (16.8%), α-thujone (11.3%), germacrene D (7.2%), camphene (6.5%), 1,8-cineole (5.8%) and β-caryophyllene (5.4%).“
[Mass propagation and essential oil analysis of Artemisia vulgaris., Govindaraj, S., Kumari, B. D. R., Cioni, P. L., Flamini, G., Journal of bioscience and bioengineering, Vol.105(3), 2008, 176-183]
„Essential Oil from wild growing Artemisia vulgaris L. originating in Erie, Pennsylvania was obtained by hydrodistillation of the aerial parts of the plant. Gas chromatographic-mass spectral analysis was used to identify the major volatiles present. Up to 22 components were detected in the essential oils. Germacrene D (25%), caryophyllene (20%), α-zingiberene (15%) and borneol (11%) represent the major components of leaf oil, while the buds were rich in 1,8-cineole (32%), camphor (16%), borneol (9%), and caryophyllene (5%).“
[Williams, Jack D., Ayman M. Saleh, and Dom N. Acharya. „Composition of the essential oil of wild growing Artemisia vulgaris from Erie, Pennsylvania.“ Natural product communications 7.5 (2012): 1934578×1200700524.] https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1934578X1200700524
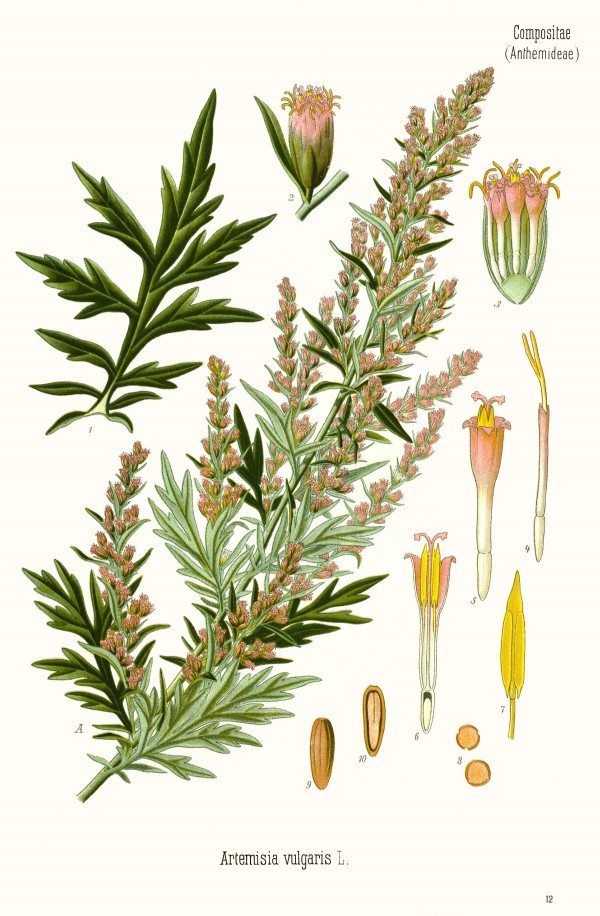
Köhler,F.E., Medizinal Pflanzen, vol.3 t.12 (1890)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=93089
Artemisia vulgaris © Rolf Marschner (2009),
www.botanische-spaziergaenge.at
