Akebia quinata (Houtt.) Decne. - syn.Rajania quinata Houtt.; Akebia micrantha Nakai. - Lardizabalaceae
木通 mu tong (chin.), アケビ Akebi (jap.), chocolate vine, five-leaf akebia, Fingerblättrige Akebie
Deciduous woody climber, 10m or higher, native to Eastern Asia (China, Korea, Japan), cultivated (as ornamental) and naturalized elsewhere; leaves palmate, petiole 4-14cm long, leaflets 4-7cm long, 1-3cm wide, upper side dark green, underside pale green; inflorecences pendulous, 4.5-9cm long; flowers fragrant; male flowers 4-11, with 3 sepals, violet, with 6-7 violet to black stamens; female ones 1-3, dark purple, occasionally green or white, with 3-4 broad elliptic, up to 1.5cm long sepals; fruits purplish, oblong to ellipsoid, 5-8×3-4cm; seeds ovoid-oblong, seed coat brown to black, shiny, pulp white.
„The roots, stems, and fruits are used medicinally.“
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200008288
„Akebia bark acts diuretic, anti-inflammatory, helps absence of menstruation and during breastfeeding. In addition, the fruit is said to heal cancer and the root to have an antipyretic effect.“
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fingerbl%C3%A4ttrige_Akebie
Dried parts (cutted crosswise in traditional manner) of the stem is known as Akebiae caulis (Japanese Pharmacopoeia). Said to act diuretic, antipyretic, antinociceptive, stimulating on ileus. Several triterpenoid saponins ('akebosides') were isolated from A.quinata containing hederagenin and oleanolic acid as triterpene aglycon.
[Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis, Springer 2010]
[The Study on the Constituents of Clematis and Akebia sp. III. The Study on the structures of Akebosides isolated from the Stem of Akebia quinata DECNE., 粂川芳広, 糸川秀治, & 藤田路一, Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin, Vol.22(10), 1974, 2294-2300]
„The antinociceptive effect was tested by hot plate-writhing and tail-flicks methods using mice, and the anti-inflammatory effect was assayed using carrageenan-induced rat edema against the following samples: the MeOH extract of A. quinata stems, its fractions, the isolated saponin, kalopanaxsaponin A, and the sapogenins hederagenin and oleanolic acid. The MeOH extract exhibited antinociceptive/anti-inflammatory effects by oral administration of 100 and 250 mg/kg doses, indicating that the MeOH extract has an antinociceptive/anti-inflammatory activity. The BuOH fraction (crude saponin) also significantly exhibited those bioactivities. Treatments with 10 and 30 mg/kg perorally of these two sapogenins produced significant antinociceptive/ anti-inflammatory effects in the rat, suggesting that the sapogenins may act as resultant active compounds. Compounds 2 and 3 inhibited dye leakage into the peritoneal cavity induced by acetic acid, and the latter was more active than the former. The anti-inflammtory effects were further supported by the reduction of carrageenan-induced lipid peroxidation and hydroxy radical content in serum. These results suggest that the antinociceptive/anti-inflammatory properties of the stem of A. quinata can be attributed to the sapogenins oleanolic acid and hederagenin.“
[Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of the saponin and sapogenins obtained from the stem of Akebia quinata., Choi, J., Jung, H.J., Lee, K.T., Park, H.J., Journal of medicinal food, Vol.8(1), 2005, 78-85]
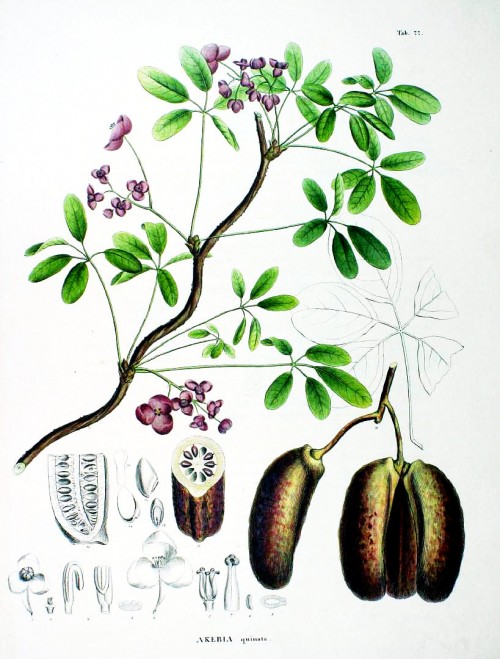
Siebold, P.F. von, Zuccarini, J.G., Flora Japonica, t.77 (1875)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=35439
