Aframomum corrorima (A. Braun) P.C.M. Jansen syn. Aframomum korarima (J.Pereira) K.Schum. ex Engl. - Zingiberaceae - Korarima, Ethiopian cardamom, false cardamom
„It is an ingredient in berbere, mitmita, awaze, and other spice mixtures, and is also used to flavor coffee. Its flavor is comparable to that of the closely related Elettaria cardamomum or green cardamom. In Ethiopian herbal medicine, the seeds are used as a tonic, carminative, and laxative.“ wikipedia
„Korarima (Aframomum corrorima) beloning to the family Zingiberaceae) was one of the major spice crop exported from Ethiopia mainly as a substitute for Indian cardamom. The plant is native to Tanzania, western Ethiopia (in the vicinity of Lake Tana and Gelemso), southwestern Sudan and western Uganda. Korarima is an aromatic, herbaceous, perennial plant producing leafy stems 1-2 metres tall from a rhizomatous rootstock. The plant resembles Indian cardamom.“
[C.K. Peethambaran, Girma Hailemichael, Haimanot Mitiku, Habtewold Kifelew, „In Search of Spices and Herbs in Ethiopia“, Spice India, Vol.29, No.7, July 2016, 4-10 In Search of Spices and Herbs in Ethiopia; accessed Aug 30 2020
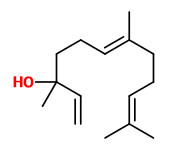
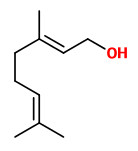
„Water-distilled essential oils from the seeds of Aframomum corrorima and A. angustifolium were analyzed by GC/MS. Fifty compounds were characterized representing 99.8% of the oil with 1,8-cineole (32.6%) and (E)-nerolidol (11.2%) as major constituents in the oil of A. corrorima.“
[Baser, K. H. C., and M. Kürkçüoglu. „The essential oils of Aframomum corrorima (Braun) Jansen and A. angustifolium K. Schum. from Africa.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 13.3 (2001): 208-209]
„The main constituents found in the seed oil were the monoterpenes 1,8-cineole (44.3%) and sabinene (17.3%), whereas sesquiterpenic structures (≥2%) such as (E)-nerolidol (17.2%), β-caryophyllene (9.7%) and caryophyllene oxide (6.9%), dominated in the husk oil.“
[Hymete, Ariaya, Jens Rohloff, and Tor‐Henning Iversen. „Essential oil from seeds and husks of Aframomum corrorima from Ethiopia.“ Flavour and fragrance journal 21.4 (2006): 642-644]
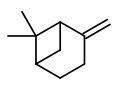
„The essential oils of the leaves, rhizomes, pods and seeds of Aframomum corrorima cultivated in the highlands of southern Ethiopia were obtained by hydrodistillation… The essential oils yield of leaves, rhizomes, pods and seeds were 0.46%, 0.69%, 0.83% and 4.30% on a w/w dry basis, respectively… The major chemical constituents in pod oil were found to be γ-terpinene (27.1 %), β-pinene (15.4%), α-phellandrene (8.5%), 1,8-cineole (6.7%) and p-cymene (6.4 %), while seed oil was predominated by 1,8-cineole (39.3%) being followed by sabinene (10.4%) and geraniol (6.8%).“
[Eyob, Solomon, et al. „Chemical composition of essential oils from fresh plant parts of Korarima (Aframomum corrorima) cultivated in the highland of Southern Ethiopia.“ Journal of essential oil research 19.4 (2007): 372-375]
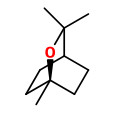
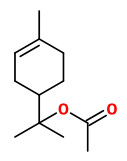
Main components of the seed oil from two samples were 1,8-cineole (34.5-37.6%), sabinene (15.2-17.0%), (E)-nerolidol (7.7-8.3%), limonene (7.6-8.4%), β-pinene (7.0-7.6%), α-terpinyl acetate (5.2-5.5%), geranyl acetate (2.6-3.9%), geraniol (2.4-4.9%), α-terpineol (2.1-2.2%), α-pinene (1.9-2.1%), and caryophyllene (0.9-1.3%).
[Menner, Michael Karl. Phytochemische und antimikrobielle Untersuchungen an den Samen von Aframomum corrorima. Diss. Graz, 2015] PDF
Main components of the seed oil were 1,8-cineole (51.8%), terpinen-4-ol (10.4%), limonene (5.4%), α-terpineol (4.9%), β-pinene (4.6%), p-cymene (4.5%), α-terpinyl acetate (3.6%), geraniol (1.9%), α-pinene (1.4%), (E)-nerolidol (1.3%), geranyl acetate (1.2%), and sabinene (1.2%). Minor compounds were e.g. linalool (0.6%), geranial (0.2%), and carvone (0.2%).
[Noumi, Emira, et al. „Chemical and biological evaluation of essential oils from cardamom species.“ Molecules 23.11 (2018): 2818] PDF

Aframomum corrorima, Ethiopia © Mitiku Muanenda (2024) CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org