Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Mentha aquatica L. f.citrata (Ehrh.) Fresen. - syn. Mentha citrata Ehrh. - Lamiaceae
bergamot mint, eau-de-cologne mint, lemon mint, orange mint, Bergamott-Minze
“Mentha citrata oil is a pale yellow or pale olive colored to almost water-white liquid of a sweet-herbaceous, somewhat fruity-fresh odor type; it resembles bergamot, but is distinctly more harsh in its terpenic topnotes, less rich in body, and without the oily-sweet, candy-like undertone of good bergamot oils. On the other hand, mentha citrata, oil presents a certain bergamot note without the citrus notes. This makes the oil more interesting in the lavender-fougere field. Its dryout has some resemblance to sage clary, but lacks the richness of that oil.”
[Arctander, Steffen. Perfume and flavor materials of natural origin, 1960, 415-416]
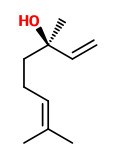
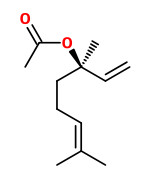
The strong lavender odor of the Bergamot Mint, Mentha citrata Ehrh., is due to two principal oil constituents, linalyl acetate and linalool, that make up 84-90% of the oil.
[Todd, W. A., and M. J. Murray. „New essential oils from hybridization of Mentha citrata Ehrh.“ Perfumary and Essential Oil Record 59 (1968): 97-102]
„Mentha citrata Ehrh. (bergamot mint; Lamiaceae) produces an essential oil containing only the acyclic monoterpenol (−)-3R-linalool and its acetate ester. A cloning strategy based upon the assumption that the responsible monoterpene synthase would resemble, in sequence, monoterpene cyclases from this plant family yielded a cDNA encoding the (−)-3R-linalool synthase. The nucleotide sequence of this monoterpene synthase is similar to those of several monoterpene cyclases from the mint (Lamiaceae) family (62–72% identity), but differs substantially from that of 3S-linalool synthase from Clarkia (41% identity; this composite gene appears to be of recent origin) and from that of 3R-linalool synthase from Artemisia (52% identity; the functional role of this gene is uncertain).“
[Crowell, Anastasia L., et al. „Molecular cloning and characterization of a new linalool synthase.“ Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 405.1 (2002): 112-121]