Benutzer-Werkzeuge
Hoya carnosa (L.f.) R.Br. - syn.Hoya motoskei Teijsm. & Binn.; Asclepias carnosa L.f. - Apocynaceae
waxflower, waxplant, porcelain flower, Porzellanblume
Epiphytic climbing shrub, up to 6m long, native to East Asia (Japan, China to Malaysia), cultivated as ornamental (indoor plant); stems robust, pale gray, smooth; leaves broadly ovate-cordate to ovate-oblong or elliptic; pseudumbels extra-axillary, globose, ca. 30-flowered; corolla white, sometimes with a pink center, fragrant. http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200018633
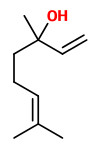
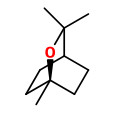
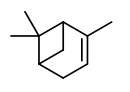
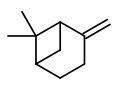
„Flowers of H.carnosa… are apperently not scented during the day but begin to produce fragrance only in the late evening… The fragrance… contained approx. 20 compounds with linalool, 1.8-cineole, β-pinene, isopentanol, α-pinene and methyl salicylate (in this order of abundance) as the main volatiles… on the first day after anthesis 45-50µg of fragrance were emitted within 24h…“
[Rhythms of fragrance emission in flowers., Matile P., Altenburger R., Planta, 174, 1988, 242-247]
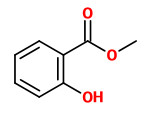
„In flowers of Hoya carnosa R. Br. the nocturnal emission of fragrance occurs according to an endogenous circadian rhythmicity… Linalool is by far the most abundant volatile of the fragrance of Hoya carnosa, but gas-liquid chromatography also allowed five additional main components, 1,8-cineole, α- and β-pinene, isopentanol, and methyl salicylate to be identified.“
[Circadian rhythmicity of fragrance emission in flowers of Hoya carnosa R.Br., Altenburger, R., Matile, P., Planta, 174(2), 1988, 248-252]
The fragrant volatiles of the typical nightly odor of H.carnosa was collected by dynamic and vacuum headspace analysis. Although collected from a non-fragrant flower at daytime, the composition of the vacuum headspace concentrate surprisingly was roughly comparable to that of the fragrant flowers at nighttime.
„Obviously, Hoya carnosa stores the volatiles produced in the daytime and releases them at night.“
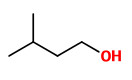
The product of the vacuum process had superior organoleptic properties, containing mainly isoamyl alcohol (isopentanol, 25%) and linalool (23%), furthermore sabinene (0.6%), benzaldehyde (1.5%), benzyl alcohol (14%), 2-phenyl ethanol (4%), methyl salicylate (2.5%), endo-2-hydroxycineole (4%) and eugenol (0.3%).
[Surburg et al., Volatile compounds from Flowers, in: Teranishi, R.;Buttery, R. G.;Sugisawa, H. Bioactive volatile compounds from plants. (Book) 1993, 169-186]
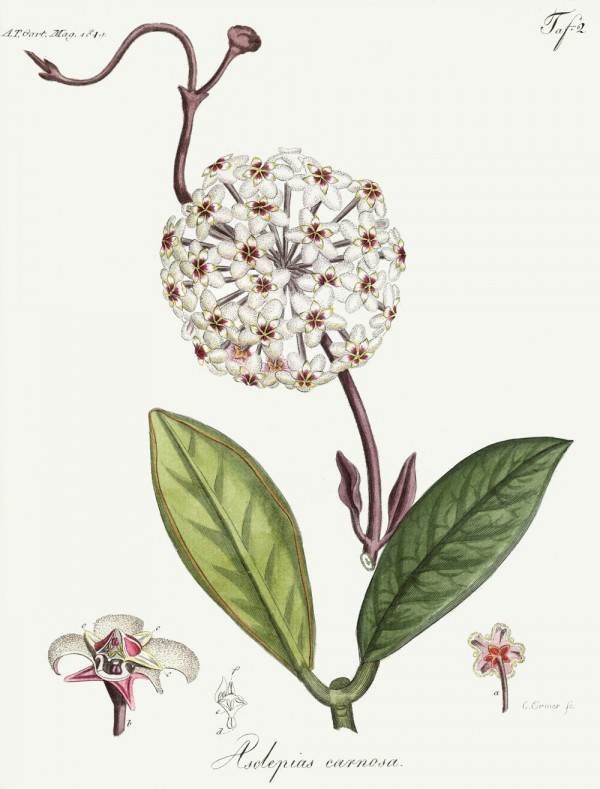

Hoya carnosa as Asclepias carnosa, Allgemeines teutsches Garten-Magazin, vol.7, t.2 (1810)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=537741