Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Cyperus articulatus L. - syn. Cyperus niloticus Forssk. - Cyperaceae
jointed flatsedge, priprioca, Priprioca
Perennial rhizomatous sedge, 1-2m tall, commonly growing in ponds, ditches, rivers, marshes, lakes and banks, with very wide pantropic distribution; „A decoction of rhizomes serves to treat aches. Remains found in archaeological sites indicate ancient uses since the Middle and Ancient Empires. The tuber has antiseptic properties and its paste is applied externally in cutaneous affections. It is used as a cane and to make essential oils.“
http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/full/164147/0
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=5&taxon_id=242101109
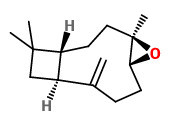 caryophyllene oxide (dry woody) | 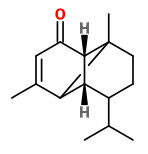 mustakone (spicy, woody, meat-broth-like, balsamic) | 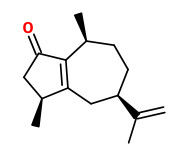 rotundone (spicy peppery) |
The bright yellow rhizome oils of C. articulatus (hydrodistillation, yield 0.5-1.0%) contained monoterpenes like α-pinene (5.7-12.9%), β-pinene (4.2-7.4%), trans-pinocarveol (3.8-7.5%), trans-verbenol (1.4-2.7%), pinocarvone (1.6-1.9%) and myrtenal + myrtenol (4.1-7.7%). Main sesquiterpenes were cyperene (0.6-4.3%), rotundene ([rotundone] 0.4-0.8%), ledol (3.2-4.6), caryophyllene oxide (4.6-13.7%), mustakone (7.3-14.5%), patchoulenone (0.4-1.6%), cyperotundone (2.1-5.4%) and α-cyperone (1.4-5.9%).
[Yield and chemical composition of the essential oil of the stems and rhizomes of cyperus articulatus L. cultivated in the state of Para, Brazil., Zoghbi, M.D.G.B., Andrade, E.H.A., Oliveira, J., Carreira, L. M.M., Guilhon, G.M.S., Journal of Essential Oil Research, 18(1), 10-12, 2006]
„The cosmetic use of this root, which grows naturally in the Amazon rainforest, is widespread in the North of Brazil, where it is part of the “banho de cheiro”, an aroma that is a key element of the Amazonian tradition.“
[A new ingredient: The introduction of priprioca in gastronomy., Atala, A., International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science, 1(1), 61-63, 2012] http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1878450X11000023
„The methanolic extract of rhizomes of Cyperus articulatus, a plant used in traditional medicine in Africa and Latin America for many diseases, possesses anticonvulsant activity in mice… that might explain its use as a traditional medicine for epilepsy in Africa.“
[Anticonvulsant properties of the methanolic extract of Cyperus articulatus (Cyperaceae)., Bum, E.N., Schmutz, M., Meyer, C., Rakotonirina, A., Bopelet, M., Portet, C., Herrling, P., Journal of ethnopharmacology, 76(2), 145-150, 2001]
„The decoction of the rhizome of Cyperus articulatus is empirically used in several African countries in the treatment of a wide variety of human diseases… The total extract of the rhizome of C. articulatus does not appear to possess either anaesthetic or paralysing effects. In contrast, spontaneous motor activity is significantly reduced by the extract… The sedative actions probably explain at least part of the therapeutic efficiency claimed for this plant in traditional medicine.“
[Sedative properties of the decoction of the rhizome of Cyperus articulatus., Rakotonirina, V.S., Bum, E.N., Rakotonirina, A., Bopelet, M., Fitoterapia, 72(1), 22-29, 2001]
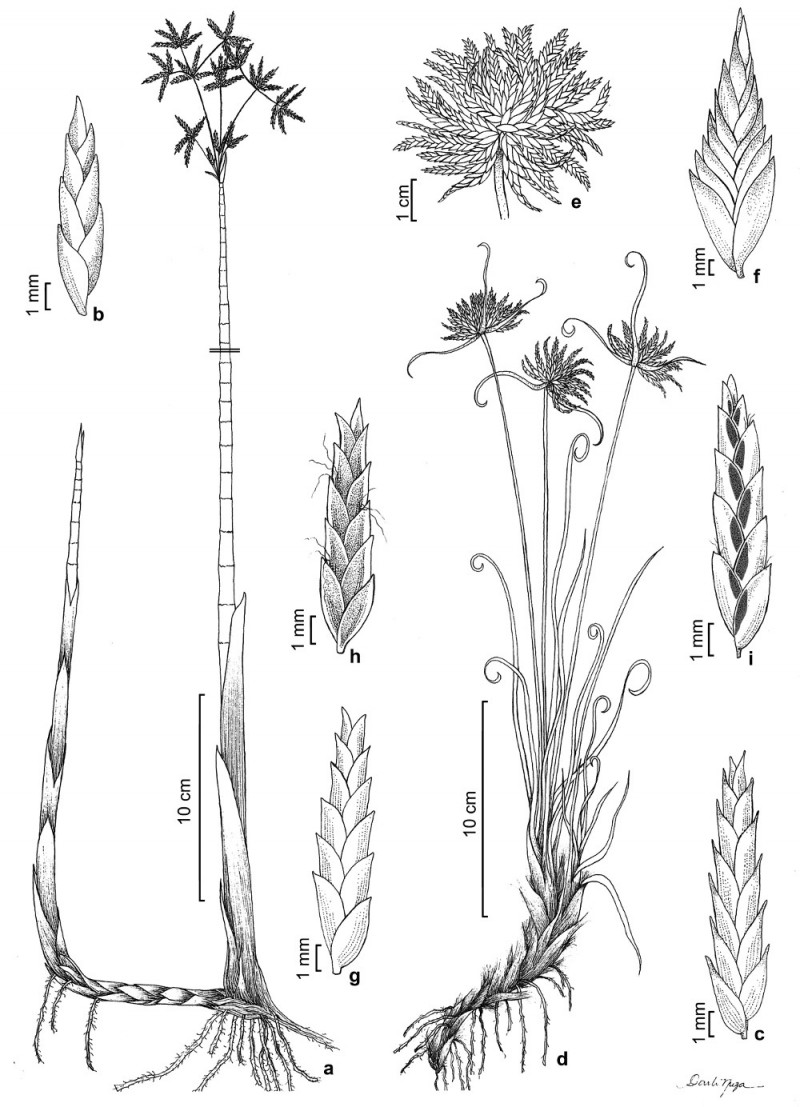
a-b. Cyperus articulatus – a. habit; b. spikelet.
[Ribeiro, André Rodolfo de Oliveira, et al. „The genus Cyperus (Cyperaceae) in Rio Grande do Norte State, Brazil.“ Rodriguésia 66.2 (2015): 571-597.] http://www.scielo.br/pdf/rod/v66n2/2175-7860-rod-66-02-0571.pdf
