Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Copaifera multijuga Hayne - Fabaceae - syn..Copaiba multijuga (Hayne) Kuntze - Brazilian copaiba, Copaiva
Large evergreen tree, native to Brazil (Amazonas, Bahia, Pará) and Bolivia (Pando).
http://www.tropicos.org/Name/13008405
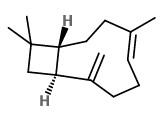
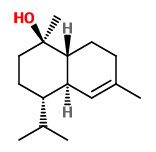
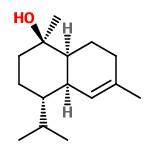
„Copaifera multijuga Hayne is one of the Copaifera species from which copaiba oil is extracted. Employed in the composition of anti-inflammatory and antiseptic products used in phytotherapy, it is also used by the fragrance industry as a fixative in perfumes, cosmetics and in products such as soaps. To identify the active aroma compounds in C. multijuga oil bouquet, GC-O-MS using AEDA (Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis) was used after the quantification of the components by GC-FID. The results obtained pointed to minor compounds such as δ-cadinene (1.9%, FD 64), δ-cadinol (0.9%, FD 128), (Z)-α-santalol (0.2%, FD 128), caryophyllene oxide (0.2%, FD 64), α-cadinol (0.1%, FD 128) and τ-muurolol (0.1%, FD 128) as the most intense compounds in the odor of the copaiba oil studied. Chiral GC-O-MS showed (+)-δ-cadinene as the only enantiomer present in the oil, with a sweet, green and refreshing aroma.“
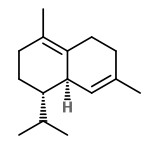
Major volatile components of the hexane extract from copaiba oleoresin were (E)-β-caryophyllene (60.2%, spicy-woody, FD 2), α-humulene (8.6%, floral-woody, FD 2), α-bergamotene (6.4%, floral-woody, FD 2), and α-copaene (4.2%, woody, FD 2).
[Sant'Anna, Beatriz MP, et al. „Characterization of woody odorant contributors in copaiba oil (Copaifera multijuga Hayne).“ Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 18.5 (2007): 984-989] http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?pid=S0103-50532007000500016&script=sci_arttext