Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Citrus × aurantium, Citrus aurantium L. - syn. Citrus aurantium var. amara; Citrus vulgaris Risso - Rutaceae
bitter orange, sour orange, bigarade, seville orange, Pomeranze, Bitterorange
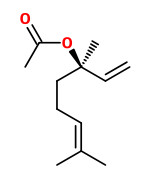
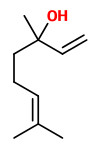
Bitter orange peel oils exhibited a very high content of limonene (87.6-95.1%). The minor components β-pinene (tr-2.4%), myrcene (1.3-1.8%), linalool (tr-1.5%), linalyl acetate (0-3.9%), α-pinene (0-0.6%) were found in almost all samples.
[Chemical variability of peel and leaf essential oils of sour orange. Marie-Laure Lota, Dominique de Rocca Serra, Camille Jacquemond, Felix Tomi, Joseph Casanova, Flavour Fragr. J. 2001; 16: 89–96]
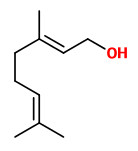
Neroli oil is the essential oil steam distilled from the flowers of C. x aurantium.
„Main volatile constituents are linalool, nerolidol and farnesol. Etymology: It. neroli, from the French-born Anna Maria de la Trémoille (1670-1722), princess of Nerola, a village near Rome. She loved the fragrance of the orange flowers, and was the first person to have them distilled. The tertiary sesquiterpene alcohol 3,7,11-trimethyl-1,6,10-dodecatriene-3-ol was first identified in neroli oil, hence the name nerolidol. Somewhat later, the isomeric alcohol 3,7,11-trimethyl-2,6,10-dodecatriene-1-ol was also identified. It was correspondingly named farnesol, from Villa Farnese, another village near Rome. “ http://www.bojensen.net/EssentialOilsEng/EssentialOils21/EssentialOils21.htm
„As most synthetic linalool contains dihydrolinalool (0.5-2.0%), this impurity can be used to determine adulteration of neroli oil with synthetic linalool. Frey (1988) showed that using the selective ion monitoring mode in GC/MS he could detect down to 50 ppm of dihydrolinalool in neroli oil, which corresponds to the addition of 0.5-1.0% synthetic linalool in the oil… Konig et al. (1992) proved through chiral GC analysis that the (R)-(-)-linalool enantiomer was predominant in neroli oil. They also found that (S)-(+)-(E)-nerolidol
was the main (>98%) enantiomer found in this same oil“
[Lawrence, Brian M. „Progress in Essential Oils-Neroli Oil, Savory Oil, Yarrow Oil and Star Anise Oil.“ Perfumer and Flavorist 28.6 (2003): 56-75] http://media.allured.com/documents/PF_28_06_056_18.pdf
„The major compounds within the hydrolate [of Citrus aurantium L. (Rutaceae) flowers (neroli) grown in Iran] obtained in the laboratory were geraniol (26.6%), α-terpineol (20.7%), linalool (15.4%) and benzene acetaldehyde (5.5%). Linalool (44.1%), methyl anthranilate (11.8%) and cis-linalool oxide (6.1%) were found in high percentages in the Hydrolate from the obtained traditional sample. 1,8-Cineol (15.9%), linalool (13.8%) and α-terpineol (6.6%) were more than other constituents in the industrially obtained hydrolate.“
[GC/MS Analysis of Citrus aurantium L. Hydrolate and its Comparison
with the Commercial Samples. Hamid Reza Monsef-Esfahani, Yaghoob Amanzade, Zahra Alhani, Homa
Hajimehdipour, Mohammad Ali Faramarzi, Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research (2004) 3: 177 -179] http://ijpr.sbmu.ac.ir/pdf_597_e28bb6bcb662fee9994b1a06bb9f7ab0.html
 linalool | 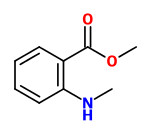 methyl N-methylanthranilate (sweet fruity) | 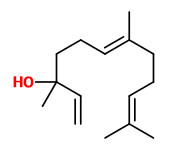 (E)-nerolidol (floral green) |  (E,E)-farnesol (floral muguet) |
„The combination of these two sesquiterpene alcohols [(+)-(E)-nerolidol 3% and (E,E)-farnesol 1%], a considerable amount of methyl N-methylanthranilate (0.1%), which resembles the odor of concord grapes, and 1H-indole (0.1%), which, on high dilution posesses a distinct exotic jasmine note, differentiate neroli from petitgrain oil. Other nitrogen-containing compounds such as 2-phenylacetonitrile (0.1%) and (2-nitroethyl)-benzene (0.15%) have been identified by Maurer. With its low treshold of 2 ng/l water (0.002ppb), 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine (1 ppm) is also important and imparts neroli with an interesting green note.“
[Scent and Chemistry, Günther Ohloff, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Philip Kraft, Wiley-VCH, 2012, 240-241]
Neroli oil showed a remarkable antibacterial activity especially against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and a very strong antifungal activity, comparable to nystatin (which was used as standard). Main components of the oil were limonene (27.5%), (E)-nerolidol (17.5%), α-terpineol (14%), α-terpinyl acetate (11.7%) and (E,E)-farnesol (8%). Methyl anthranilate was found at 1.2%.
[Chemical Composition and in vitro Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Citrus aurantium L. Flowers Essential Oil (Neroli Oil), Haj Ammar, A. Lebrihi, F. Mathieu, M. Romdhane, F. Zagrouba, Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 15(21), 2012, 1034-1040] http://scialert.net/fulltext/?doi=pjbs.2012.1034.1040
Petitgrain Essential Oil is made by steam distillation of the leaves and sometimes the twigs of the bitter orange tree.
„Bitter orange petitgrain oil showed a high content of oxygenated compounds which varied from 91% to 96%. Linalyl acetate, which represented more than 50% of the whole oil, and linalool, which ranged from 22% to 33%, were the main components. Limonene, (E)-β-ocimene, myrcene and β-pinene were the highest monoterpene hydrocarbons. Twelve sesquiterpene hydrocarbons were identified. β-Caryophyllene is the most representative of this fraction.“
[Italian Citrus Petitgrain Oils. Part I. Composition of Bitter Orange Petitgrain Oil. Luigi Mondello, Giovanni Dugo, Paola Dugo, Keith D. Bartle, Journal of Essential Oil Research, Vol.8 (6) 1996, 597-609]
Enantiomerically pure or nearly pure (R)(-)-linalyl acetate was detected in petitgrain oil of Citrus aurantium L. using a chiral capillary column.
[Ravid, Uzi, Eli Putievsky, and Irena Katzir. „Chiral gc analysis of enantiomerically pure (R)(-)‐linalyl acetate in some lamiaceae, myrtle and petitgrain essential oils.“ Flavour and fragrance journal 9.5 (1994): 275-276] see also
[Dugo, Giovanni, et al. „Characterization of oils from the fruits, leaves and flowers of the bitter orange tree.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 23.2 (2011): 45-59]
„In addition to linalool, the other important alcohols are geraniol (2.5%), nerol (0.4%), α-terpineol (5.6%), (+)-(R,E)-nerolidol (0.05%) and the intensely woody smelling (+)-spathulenol and (+)-isospathulenol (0.03%)… Although more than 100 carbonyl compounds found in petitgrain oils account for only 0.37%, their importance is unquestioned, among them high-impact compounds as β-ionone (5 ppm) and β-damascenone (2 ppm) that occur in concentrations way above their odor tresholds (0.009 and 0.007 ppb, resp.)…
Another important constituent is 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine with its typical galbanum-like, green note that can be found together with ten other substituted pyrazines. The concentration of [it] in petitgrain oil is 1 ppm, which exceeds its odor treshold by a million times.“
[Scent and Chemistry, Günther Ohloff, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Philip Kraft, Wiley-VCH, 2012, 238]
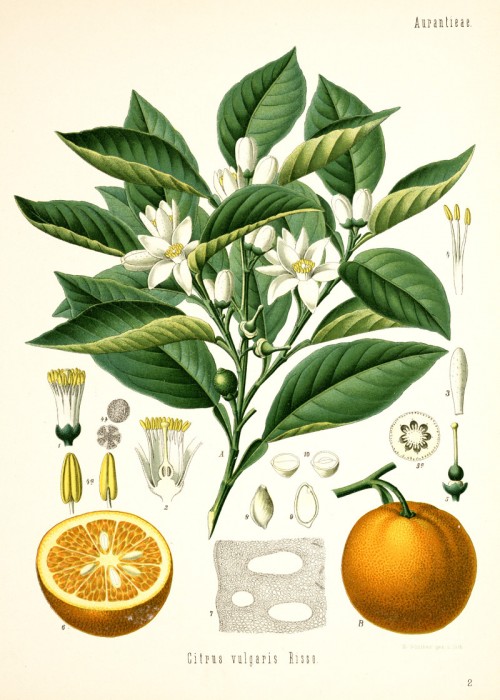
Köhler,F.E., Medizinal Pflanzen, vol.1, t.2 (1887) [W.Müller]
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=249703