Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Cinnamomum glaucescens (Nees) Hand.-Mazz. - syn.Cinnamomum cecidodaphne Meisn.; Tetranthera glaucescens Buch.-Ham. - Lauraceae
sugandha kokila, Himalaya cinnamon
Evergreen tree, native to Himalaya (Nepal to Bhutan), India.
https://www.gbif.org/species/4175703
„Using steam distillation, the dried berries of Cinnamomum glaucescens produce the essential oil commonly known as sugandha kokila oil, which is yellow in colour and has a camphoraceous, spicy aroma… However, Non-timber forest products, such as Cinnamomum glaucescens, are over harvested, and if the current rate of collection occurs, may disappear from Nepalese forests.“
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sugandha_Kokila_Oil
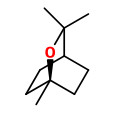
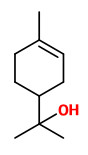
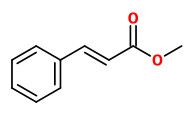
Major components of the commercially available essential oil of Cinnamomum glaucescens fruits (with seeds) were 1,8-cineole (13%), methyl cinnamate (14%), α-terpineol (7%) and many mono- and sesquiterpene hydrocarbons. The pericarp oil consisted mainly of 1,8-cineole (56%) and α-terpineol (10%).
[Adhikary, S. R., et al. „Investigation of Nepalese essential oils. I. The oil of Cinnamomum glaucescens (Sugandha Kokila).“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 4.2 (1992): 151-159]
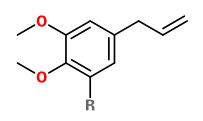
The essential oil of Cinnamomum glanduliferum leaves contained elemicin (92.9%) as predominant component.
[Baruah, Akhil, and Subhan C. Nath. „Leaf essential oils of Cinnamomum glanduliferum (Wall) Meissn and Cinnamomum glaucescens (Nees) Meissn.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 18.2 (2006): 200-202]
Main components of commercial oils were 1.8-cineole (21.9-25%), methyl cinnamate (8.7-13.4%), α-phellandrene (4.6-10.8%),and α-terpineol (2.8-5.0%).
"Sugandha Kokila Essential Oil" aromatics.com GC/MS provided, retrieved 2017-11-25.