Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
Cinnamomum burmanni (Nees & T. Nees) Nees ex Blume - syn.Cinnamomum mindanaense Elmer; Laurus burmanni Nees & T. Nees - Lauraceae
Indonesian cinnamon, (Batavia, Padang) cinnamon; Batavia cassia, (Java, Padang, Korintle) cassia; 阴香 yin xiang (chin.), Birmazimt (-Baum)
Tree, up to 14m high, native to Southeast Asia (China to Indonesia); bark brown outside, red inside, cassia-scented; leaves glaucous green and opaque abaxially, green and shiny adaxially, ovate or oblong to lanceolate, leathery, glabrous, triplinerved, midrib and basal lateral veins very elevated abaxially, conspicuous adaxially; flowers green-white, ca. 5mm; fruit ovoid, ca. 8×5mm.
„The dried bark is a source of an important spice, which is used as a substitute for cassia bark. The wood is heavy, soft, finely grained, and used for house construction. The leafy branchlets contain volatile oil. Three types of the oil are found in Yunnan: linalol type (linalol ca. 57%), citral type (citral ca. 77%), and cineole type (cineole ca. 47%).“
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200008695
Main components of the essential oils from leaves of Mei Pian tree (Cinnamomun burmannii B1 physiological type grown in Guangdong province, China), obtained by hydro-distillation, were D-borneol (78.6%), bornyl acetate (3.2%), (-)-spathulenol (2.6%), and 1,8-cineole (1.9%).
[A new source of natural D-borneol and its characteristic., Chen, L., Su, J., Li, L., Li, B., Li, W., J Med Plants Res, 5, 2011, 3440-7] http://www.academicjournals.org/article/article1380631255_Chen%20et%20al.pdf
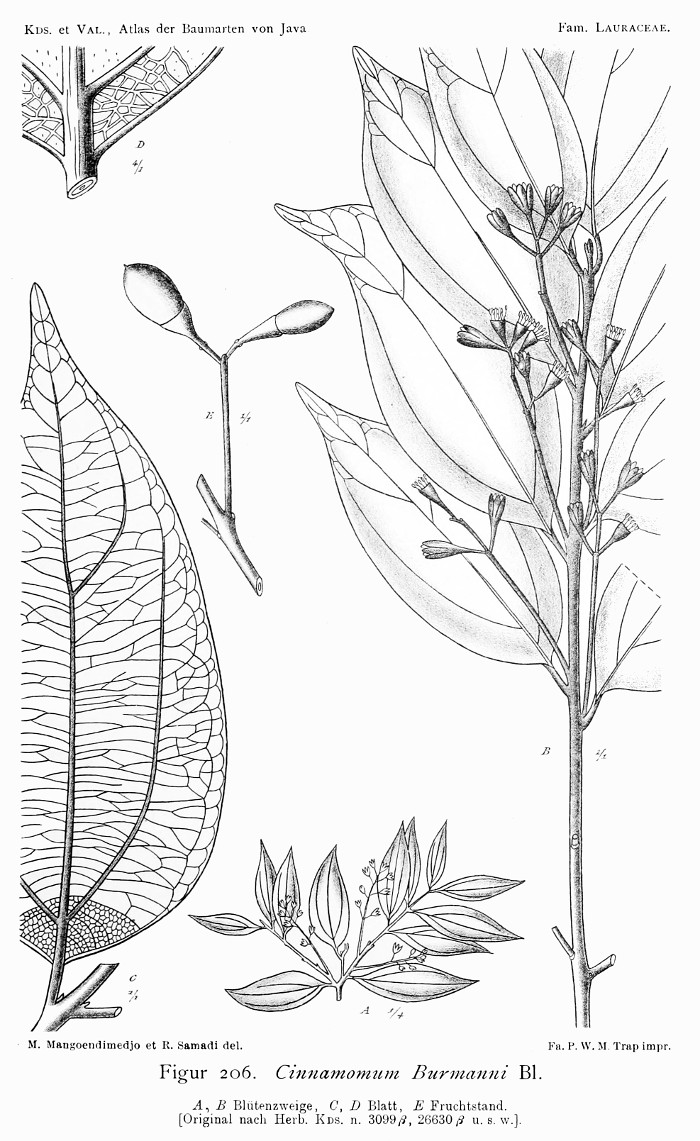
Koorders,S.H., Valeton,T., Atlas der Baumarten von Java, vol.2 t.206 (1814) [M.Mangoendimedjo & R.Samadi]
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=244153