Sophora flavescens Aiton - syn.Sophora angustifolia Siebold & Zucc. - Fabaceae - 苦参 ku shen (chin.), shrubby sophora
Deciduous subshrub, up to 1.5m high, with annual shoots; native to Asia from Mongolia to Japan; leaves odd-pinnate; leaflets narrowly ovate to oblong, acuminate; racemes terminal; corolla white or pale yellow (var.flavescens and kronei) or purple-red or red (var.galegoides).
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200012319
Radix Sophorae flavescentis (kushen, lightyellow sophora root) is a TCM listed in the Pharmaopoeias of China and Japan. It is used for the treatment of arrhythmia, diarrhea, gastraointestinal haemorrhage, skin disorders, eczema, jaundice, vaginits and asthma.
[Radix Sophorae flavescentis - Kushen, Bauer, R., Xiao, P.G., in: Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Herbal Medicines, Springer Vienna, 2011, 743-754]
The root contains the quinolizidine alkaloids matrine and matrine oxide, which are also found in decoctions of it. Among the twenty compounds isolated from the dichloromethane extract are three pterocarpan derivatives, eleven flavanones, two flavanonoles, two chalcones, a chroman, a isoflavone and one coumarin. The flavanoid fraction inhibited 5-LOX, and 2'-methoxy kurarinone (isokurarinone) was the most effective compound. Sophoraflavanon G (norkurarinone) inhibited 5-LOX as well as COX-1 and COX-2 (as potent as indometacin reference).
[Phytochemische und pharmakologische Untersuchungen der Wurzeln von Sophora flavescens, unter besonderer Berücksichtigung ihrer Wirkung auf die Leukotrien-und Prostaglandinbiosynthese., Schwarte, A., Cuvillier Göttingen. 2002]
http://docserv.uni-duesseldorf.de/servlets/DerivateServlet/Derivate-2201/201.pdf
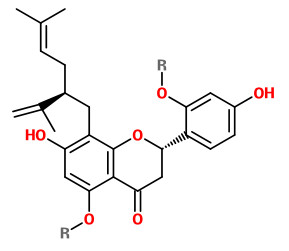 Sophoraflavanon G (R= H), isokurarinone (R= CH3)
Sophoraflavanon G (R= H), isokurarinone (R= CH3)
„A qualitative composition and a quantitative content of phenolic compounds of underground and above-ground parts of Sophora flavescens Soland. (the Fabaceae family) growing in Russia (Transbaikalia, Primorsky Krai, Aga Buryat Autonomous District) were studied. Eleven compounds were isolated from the roots and rhizomes: kushenol A, isokurarinone, kuraridine, sophoraflavanone G, kurarinone, isoxanthohumol, umbeliferon, and, for the first time, scopoletin, ferulic, caffeic, and chlorogenic acids. Ten phenolic compounds were identified in the herb of S. flavescens: cynaroside, cosmosiin, caffeic acid, and, for the first time, apigenin, luteolin, quercetin, umbelliferone, rutin, chlorogenic, and neochlorogenic acids. Dominant compounds in the underground part were kurarinone and sophoraflavanone G, and in the above-ground part, cynaroside and rutin.“
[Phenolic compounds of Sophora flavescens Soland. of Russian origin., Olennikov, D.N., Tankhaeva, L.M., Pankrushina, N.A., Sandanov, D.V., Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry, Vol.39(7), 2013, 755-760]

Sophora flavescens, Author: Qwert1234, GFDL
source: ja.wikipedia.org