Nymphaea caerulea Savigny - syn. Nymphaea calliantha Conard.; Nymphaea nouchali Burm. f. var. caerulea (Sav.) Verdc. - Nymphaeaceae
blue lotus, blue Egyptian lotus, Blauer Lotus, Blaue Ägyptische Seerose
„Its original habitat may have been along the Nile and other parts of East Africa. It spread more widely in ancient times, including to the Indian subcontinent and Thailand… This lotus has been used to produce perfumes since ancient times; it is also used in aromatherapy.“
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nymphaea_caerulea
„… Nymphaea caerulea with all those common names that captivated the hearts of the Egyptians, both with its appearance and with its intensely sweet aromatic-floral, yet refreshing, rather hyacinth-like perfume and its association with the sun god Ra…not even a specialist can imagine the synesthetic experience offered by these wonderful blue flowers.“
Not a special compound, but a special delicate equilibrium of ten or so compounds makes this scent by the interaction of benzyl acetate (26.0%), anisaldehyde (0.1%), anisyl alcohol (0.2%), (E)-cinnamyl acetate (1.7%), and cinnamyl alcohol (1.3%), together with a series of derivatives of (E,E)-undeca-3,5-dien-2-one (0.2%), (E)-undec-5-en-2-one (1.7%), (E)-undec-5-en-2-ol (0.2%), (E)-undec-5-en-2-yl acetate (0.3%), and a distinct aura is added by α-ionone and β-ionone.
[Meaningful Scents around the World, Roman Kaiser, Zürich 2006, 114-116 and 245]
The most abundant volatile compounds (dynamic headspace SPME on PDMS/DVB) of living water lily were 6,9-heptadecadiene (40.1%), pentadecane (15.5%), 8-heptadecene (15.3%), benzyl acetate (10.4%), benzyl alcohol (4.4%), heptadecane (2.2%), 2-heptadecanone (2.2%), (E)-β-farnesene (1.5%), and β-sesquiphellandrene (1.3%). Minor components were e.g. benzaldehyde (0.05%), decanal (0.71%), undecanal (0.11%), ethyl decanoate (0.12%), α-ionone (0.16%), β-ionone (0.24%), and farnesene (0.47%).
[Tsai, Feng-Jie, et al. „Determination of Volatile Components from Live Water Lily Flowers by an Orthogonal-Array-Design-Assisted Trapping Cell.“ Applied Sciences 9.7 (2019): 1269]
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/9/7/1269/pdf
A commercial 'Lotus Blau absolue' (Sri Lanka/Essence Pur) contained benzyl alcohol (27.4%), geranylgeraniol (14.9%), 6,9-heptadecadiene (13.6%), phytol (7.95), 8-heptadecene (4.5%), benzoic acid (2.9%), pentadecane (2.3%), 2-heptadecanone (2.3%), anisyl alcohol (2.2%), and squalene (2.2%) as main components.
Minor components were e.g. benzaldehyde (0.18%), benzyl acetate (0.31%), farnesene (0.37%), α-ionone (0.1%), phenylethanol (0.17%), β-ionone (0.44%), dihydro beta ionone (0.1%), methyleugenol (0.09%), 2-pentadecanone (0.15%), anisaldehyde (0.29%), eugenol (0.37%), and benzyl benzoate (0.46%).
[GC-MS of 'Lotus Blau absolue' Essence Pur; Andreas Kraska 20210816]
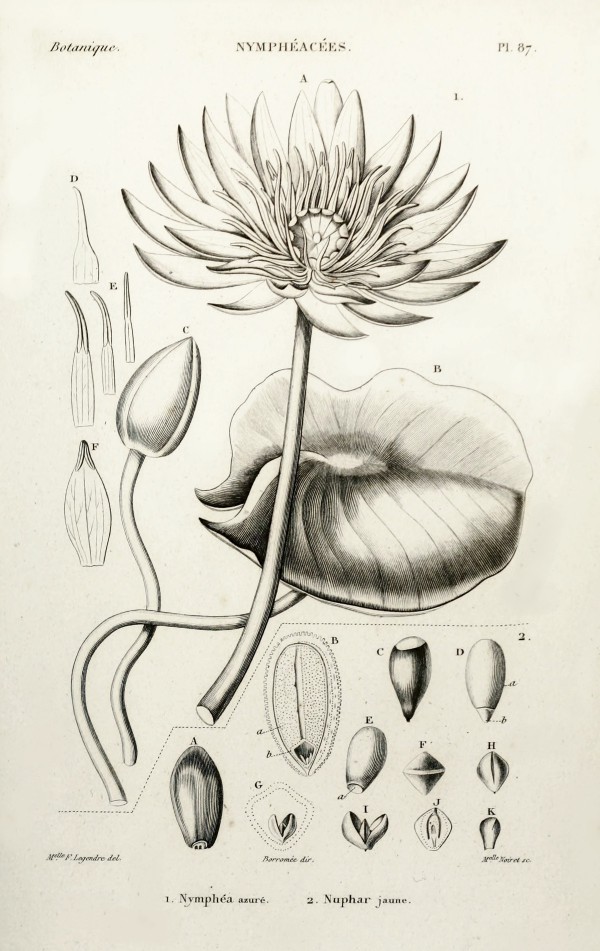
Nymphaea caerulea as 'Nymphaea azure'
Spach, E., Histoire naturelle des végétaux, Atlas (black & white edition), t 87, fig 1 (1834-1847) [M.elle F. Legendre]
http://botanicalillustrations.org/illustration.php?id_illustration=174561
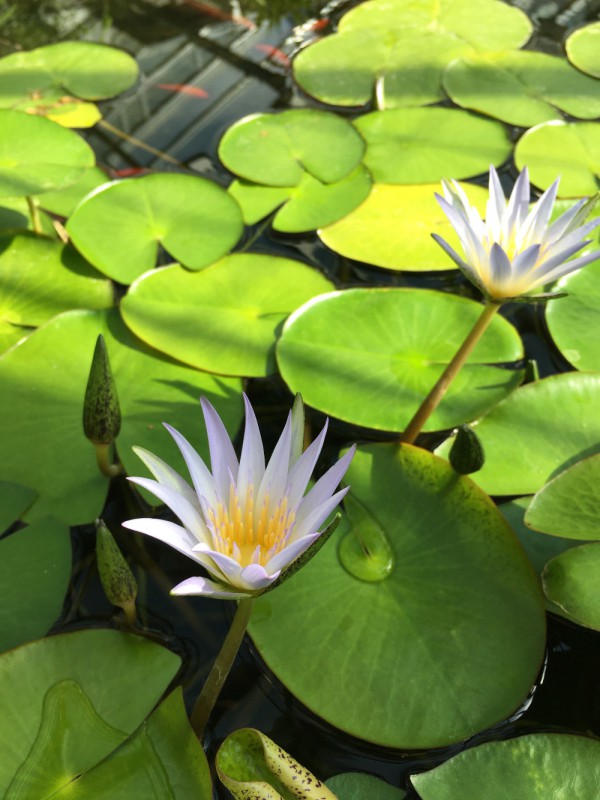

Nymphaea caerulea, Gruson Gewächshäuser Magdeburg (2022)
CC BY-SA 3.0, Author: Andreas Kraska