Leonurus japonicus HOUTT. - syn.Leonurus heterophyllus Sweet; Leonurus artemisia (Loureiro) S.Y.Hu; Leonurus sibiricus auct. pl. - Lamiaceae
益母草 yi mu cao (chin.), Chinese Motherwort, Chinesisches Mutterkraut, (Japanischer) Löwenschwanz, Sibirisches Herzgespann
Annual or bienniel herb, 30-120cm high, native to East and Southeast Asia; lower stem leaf blades ovate, 3-palmatipartite; floral leaves linear to linear-lanceolate; flowers sessile, calyx tubular-campanulate (6-8 mm), corolla white or reddish to purplish red. http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=210000972
„It is one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine, where it is called yìmǔcǎo (Chinese: 益母草), literally „beneficial herb for mothers“.“ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leonurus_japonicus
The plant has been used for centuries in Korea and is said to be the most important crude drug in gynecological medicine. It is officially listed in the Korean Pharmacopoeia. Aerial parts contain labdane-type diterpenes (leosibirinone, 3α-Acetoxy-15-O-methylleopersin C), and flavonoid(-glycoside)s (nicotiflorin, rutin, genkwanin, tiliroside, cosmosiin, isoquercitrin).
[Labdane diterpenes and flavonoids from Leonurus japonicus. Seo, H. K., Kim, J. S., & Kang, S. S., Helvetica Chimica Acta, Vol.93(10), 2010, 2045-2051]
http://www.ncshm.re.kr/erp/erpmenus/research_result/uploadfiles/%EC%9D%B5%EB%AA%A8%EC%B4%88-%EA%B0%95%EC%82%BC%EC%8B%9D.pdf
„Leonurine is a prominent pharmacologically active guanidine alkaloid (4-{[amino(imino)methyl]amino} butyl-4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoate), mainly exerting cardiovascular, hypotensive, uterotonic, and neuroprotective effects. It is commonly regarded as the predominant active principle of Leonurus and Leonotis drugs (subfamily Lamioideae), though its presence has only been unambiguously proven for the aerial parts of Leonurus japonicus Houtt. (yimucao/Chin.Ph.,DAB), used in TCM/Kampo for the treatment of various gynaecological and cardiovascular disorders.“
[Leonurus japonicus, Leonurus cardiaca, Leonotis leonurus: A novel HPLC study on the occurrence and content of the pharmacologically active guanidino derivative leonurine., Kuchta, K., Ortwein, J., Rauwald, H.W., Die Pharmazie-An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 67(12), 2012, 973-979]
„Yimucao oil was mainly made up of diterpenes (32.77%) and sesquiterpenes (45.37%), with phytone (19.02%), phytol (13.75%), caryophyllene oxide (11.49%) and β-caryophyllene (9.89%) being the most significant constituents. Other sesquiterpenes that were present in appreciable amounts were spathulenol (5.31%), α-caryophyllene (3.38%) and isocaryophyllene (3.00%).“
[Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of essential oils from different parts of Leonurus japonicus Houtt. Xiong, L., Peng, C., Zhou, Q. M., Wan, F., Xie, X. F., Guo, L., … & Dai, O., Molecules, Vol.18(1), 2013, 963-973]
The dried herb, Chinese drug name PhPRC 2010: Leonuri japonici herba, yimucao, 益母草, is used to treat menstrual pain, premenstrual syndrome, pain after birth, myoma, infertility, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, urinary tract infections, and edema. It should be used with caution (or should be avoided) during pregnancy and child birth. PhPRC 2010 demands min. 0.050% leonurine hydrochloride, min. 0.50% stachydrine hydrochloride.
http://www.lfl.bayern.de/mam/cms07/publikationen/daten/merkblaetter/chinese_medicinal_plants__cultivated_bavaria_lfl-merkblatt.pdf
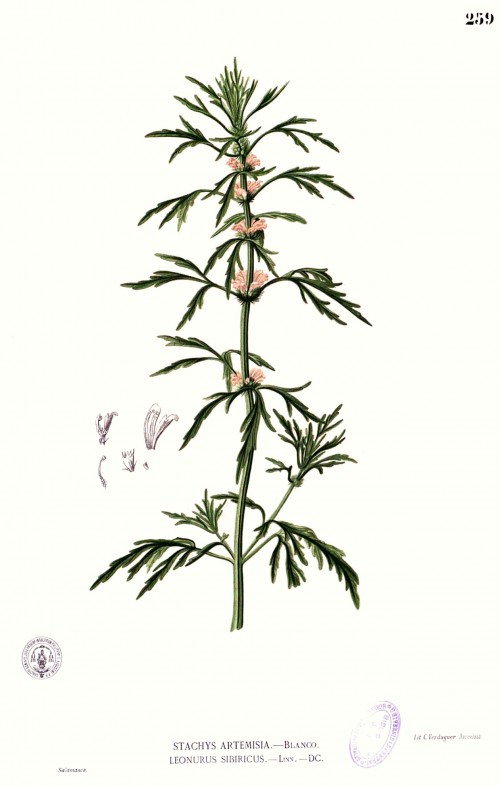
L.japnonicus as Leonurus sibiricus; Blanco, M., Flora de Filipinas, t.259 (1875)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=592986