Juniperus occidentalis Hook. - Cupressaceae - Western Juniper, Sierra Juniper, Westamerikanischer Wacholder
Shrub or tree, native to western North America. (US: Oregon and Washington).
„The essential oil obtained from the heartwood is used as an fragrance component in soaps, sprays and disinfectants as well as as an immersion oil in microscopy.“ https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Westamerikanischer_Wacholder
„The crude oil, as recovered, was a dark-red, opaque liquid. The odor was somewhat harsh, suggestive of the odor of the foliage or bark… [Wood] Oil recovery averaged around 1.4%, of which about 15-40% was cedrol… The oils from high-pressure runs, when treated by the Raybak process (Guentherp. 300 Vol I) yielded about 20-25% of the weight of oil as crystalline cedrol.“ [Kurth, Ervin Frank, and John Daryl Ross. „Volatile oil from western juniper.“ (1954)] https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/downloads/c247ds142
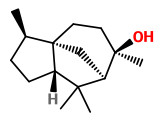
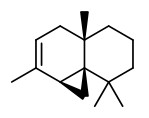
Main components of the essential oil extracted from the wood of J.occidentalis var.occidentalis were cedrol (38.9%), thujopsene (18.9%), α-cedrene (8.8%), β-cedrene (2.6%), widdrol (1.6%), and cuparene (1.5%).
[Adams, Robert P. „Investigation of Juniperus species of the United States for new sources of cedarwood oil.“ Economic Botany 41.1 (1987): 48-54] see also ref. in: http://www.juniperus.org/uploads/2/2/6/3/22639912/99-1991sprverlag159-173.pdf
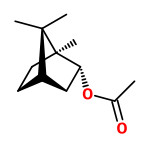
Main components of the essential oil extracted from the foliage, were sabinene (13.1%), m-cymene (9.2%), cis-sabinene hydrate (2.2%), linalool (3.7%), camphor (3.8%), borneol (4.3%), 4-terpineol (19.7%), and bornyl
acetate (24.1%).
[Duringer, Jennifer M., et al. „Acute aquatic toxicity of western juniper (Juniperus occidentalis) foliage and Port Orford cedar (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana) heartwood oils.“ Environmental monitoring and assessment 170 (2010): 585-598]
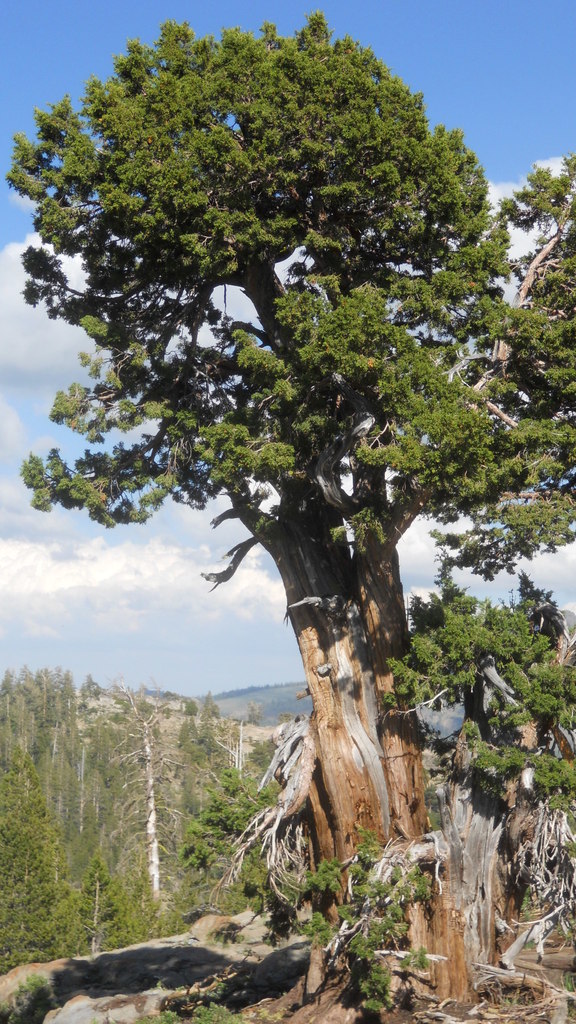

Juniperus occidentalis © Mr StobbeCC BY-SA 2.0
http://www.flickr.com/photos/25788489@N07/4828541416