Inga marginata Willd. - Mimosaceae - ingá feijão, inga mirim (braz.)
Other names: Guabilla, Guama del rio (Columbia), ingai (Paraguay), pacae (Bolivia), shimbillo (Peru), warakusa (Guiana) http://www.tradewindsfruit.com/content/guabilla.htm
„Inga marginata Willd. is a Neotropical tree species that can reach up 20m in height. It is a common species from Mexico to Argentina, but with low population density. The species ranges from 0-1950 meters above sea level and inhabits disturbed primary forests, gallery forest, lowland and montane rainforest, and along riversides and roads. It is used for its edible fruits, wood, and is commonly planted as a shade tree in coffee plantations… Inga marginata was a mass-flowering species and produced flowers twice a year, with a synchronic flowering period between trees… The flowers are arranged in raceme-shaped inflorescences at the apices of the branches, they are composed of many brush-type flowers with reduced perianth parts, and numerous white stamens fused at the base. “
[Marín-Gómez, O. H., M. M. López-García, and M. Girón Vanderhuck. „Floral visitors of Inga marginata Willd.(Mimosaceae) in a coffee agroecosystem of Quindío, Colombia.“ Tropical Ecology 57.4 (2016): 649-654]
see also Brazilian Flora 2020 project - Projeto Flora do Brasil 2020 as well as
STRI Research Portal - Inga marginata
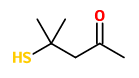 4-mercapto-4-methylpentane-2-one (4-MMP)
4-mercapto-4-methylpentane-2-one (4-MMP)
„The bottle-brush-like white inflorescences covering these trees emit an extremely diffusive fruity-floral scent which is characterised by a strong blackcurrant note, the latter showing a tendency to cat urine, if the nose is too close. This note could be localised by sniffing at the exit of the GC and, after pre-concentration of the corresponding region, a mass spectrum could be recorded which was identical to that of 4-mercapto-4-methyl-pentan-2-one, the adduct of hydrogen sulfide to mesityloxide. This mercapto-ketone shows an extremely low perception threshold of around 0.05ng/l air and has been described as an aroma impact product of sauvignon wines. Furthermore, it has been identified as one of the many compounds formed during Maillard reactions involving cysteine, ribose and phospholipid.“ Main components of the floral scent, trapped on Porapak, were caryophyllene (47.2%), E-ocimene (17.0%), linalool (6.9%), and the linalool oxides (cis+trans furanoid and pyranoid). Minor components were e.g. mesityl oxide (0.2), 4-mercapto-4-methylpentane-2-one (0.00001%), 2-methyl butyraldehyde oxime (0.3%), 2-methyl butyraldehyde oxime methyl ether (0.2%), 2-methyl butyronitrile (0.05%), and 2-methylpropionaldehyde oxime methyl ether (0.2%).
[Kaiser, Roman. „Scents from rain forests.“ CHIMIA International Journal for Chemistry 54.6 (2000): 346-363]
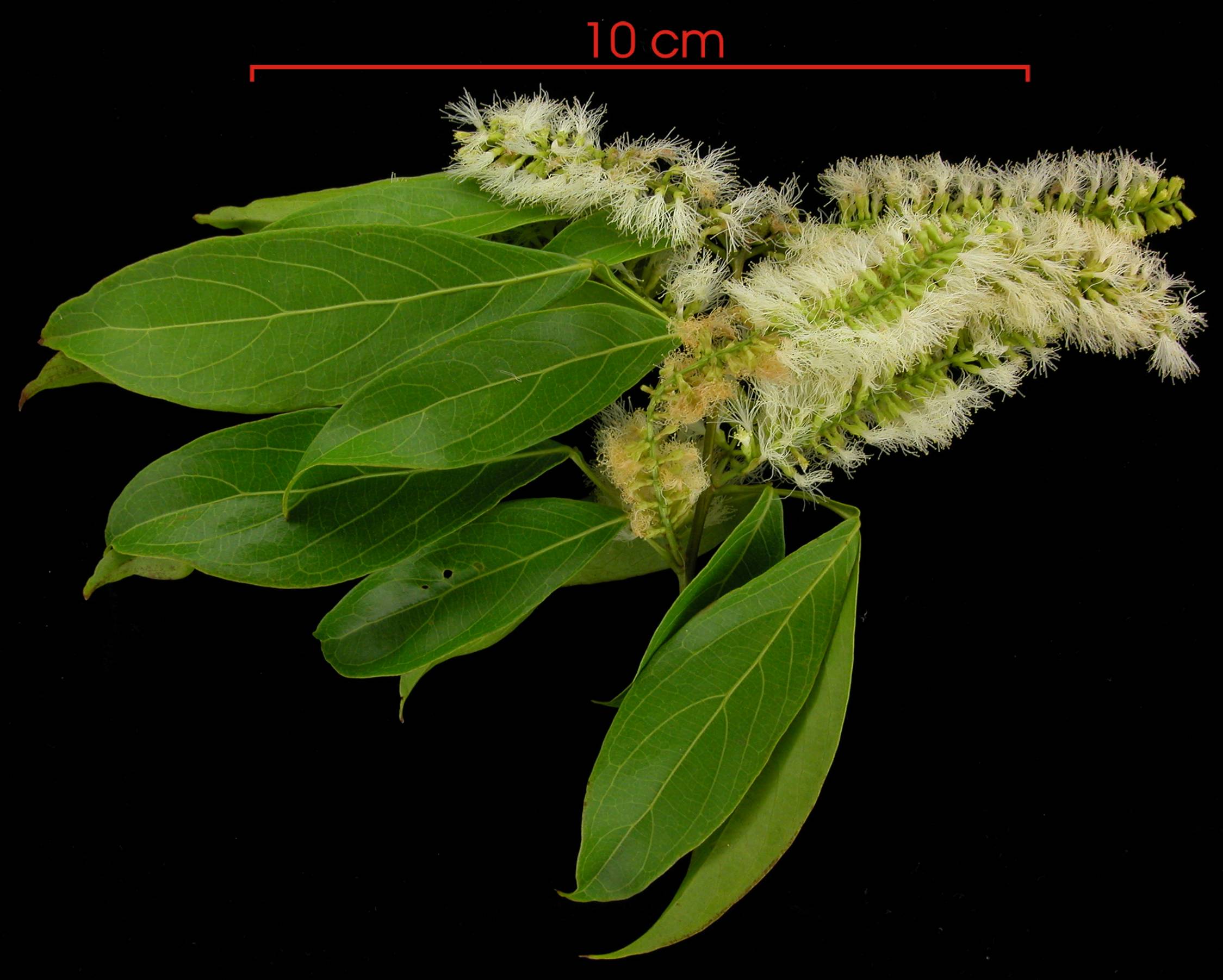

Flowers and leaves; Photograph by: Environmental Sciences Program, Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute
© Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute Useful Tropical Plants: Inga margianta images