Fraxinus ornus L. - Oleaceae- flowering ash, manna ash, Manna-Esche, Blumenesche
Deciduous tree, up to 25m high, native to South Europe, West Asia; leaves opposite, odd pinnate, up to 20cm long, leaflets 5-9, ovate-lanceolate, serrate; flowers in dense panicles, petals creamy white; fruit a one-seeded nut (samara) with one wing (up to 2cm long).
„F.ornus yields manna (Manna cannelata) - fried sugary exudate that flows after insect damag or after deliberate incisions of the bark during warm, dry weather… Manna is composed mainly of D-mannitol (70-90%), with smaller amounts of D-glucose, D-fructose and oligosaccharides… Manna is a useful laxative, especially when a soft stool is required (in cases of painful haemorrhoides, anal fissures or after surgery).“
[Medicinal Plants of the World. Ben-Erik Van Wyk and Michael Wink, Pretoria 2004, 147]
„Fraxinus ornus bark is used in the traditional medicine for wound healing and treatment of inflammation,
arthritis and dysentery. Biological studies on crude extract, many of its constituents and some extractives have revealed significant antimicrobial, antioxidative and photodynamic damage prevention, wound healing, anti-
inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antiviral activities providing a support to the ancient claims. Chemical studies on bark, leaves and flowers of F. ornus have shown the presence of many compounds belonging mainly to the groups of hydroxycoumarins, secoiridoid glucosides, phenylethanoids and flavonoids. F. ornus is rich in hydroxycoumarins. Esculin, esculetin [6,7-dihydroxycoumarin], fraxin and fraxetin are the main components of the bark.“
[Pharmacological activities and biologically active compounds of Bulgarian medicinal plants., Ivancheva, S., Nikolova, M., Tsvetkova, R., Phytochemisry: Advances in research. Kerala: Signpost, 2006, 87-103] http://www.trnres.com/ebook/uploads/imperato/T_1231133680Imperato-4.pdf
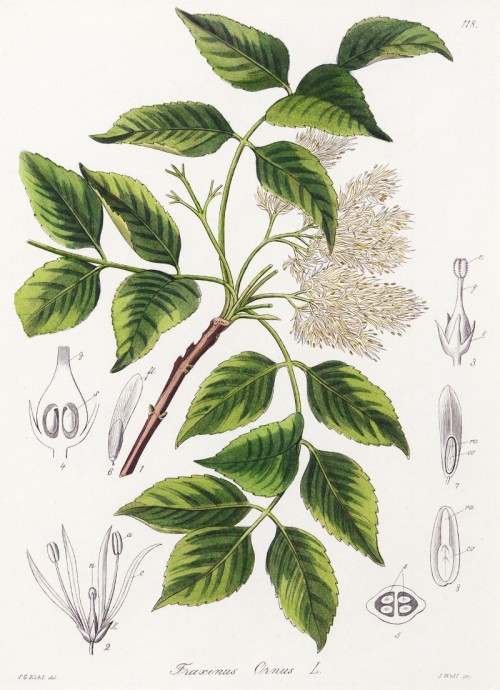
Kohl,F.G., Die officinellen Pflanzen der Pharmacopoea Germanica, t.118 (1891-1895)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=444256