Carum carvi L. - Apiaceae - caraway, Kümmel, Echter Kümmel, Wiesen-Kümmel
Annual or biennial herb, up to 1m tall, native to Asia, Europe and North Africa, mainly cultivated in the Netherlands, Finland, Hungary, Morocco, Iran, India and Russia; basal leaves oblong-lanceolate, 2-3 pinnate, upper ones linear, much divided; umbels 2.5-6 cm across, flowers white to pink; fruit oblong-ellipsoid, 3-5 × 1-2 mm, vittae 1 in each furrow, 2 on commissure.
http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=200015475
Main volatile compounds of the floral fragrance of Carum carvi, collected at PorapakQ, were limonene (15%), β-caryophyllene (16%), and E-β-farnesene (58%).
[Volatile compounds from flowers of six species in the family Apiaceae: bouquets for different pollinators? Borg-Karlson, A.K., Valterová, I., Nilsson, L.A., Phytochemistry, Vol.35(1), 1993, 111-119]
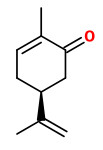
„The biosynthesis of the monoterpenes limonene and carvone in the fruit of caraway (Carum carvi L.) proceeds from geranyl diphosphate via a three-step pathway. First, geranyl diphosphate is cyclized to (+)-limonene by a monoterpene synthase. Second, this intermediate is stored in the essential oil ducts without further metabolism or is converted by limonene-6-hydroxylase to (+)-trans-carveol. Third, (+)-trans-carveol is oxidized by a dehydrogenase to (+)-carvone…
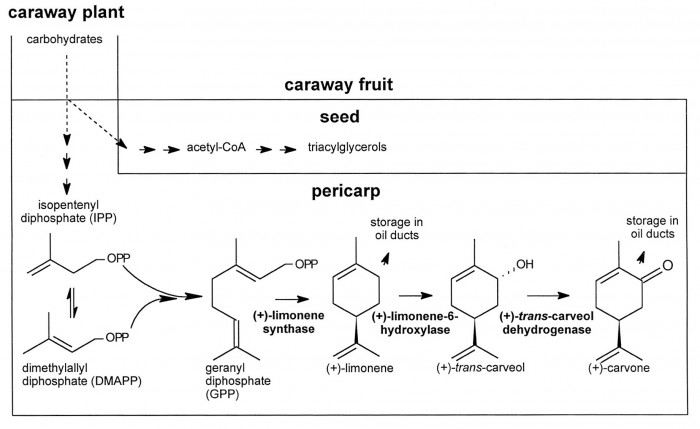
In the youngest stages, when limonene-6-hydroxylase is undetectable, only limonene was accumulating in appreciable levels. The appearance of limonene-6-hydroxylase correlates closely with the onset of carvone accumulation. At later stages of fruit development, the activities of all three enzymes declined to low levels.“
[Biosynthesis of the Monoterpenes Limonene and Carvone in the Fruit of Caraway I. Demonstration of Enzyme Activities and Their Changes with Development., Bouwmeester, H.J., Gershenzon, J., Konings, M.C., Croteau, R., Plant Physiology, 117(3), 1998, 901-912] http://www.plantphysiol.org/content/117/3/901.full
Dependent on planting conditions and variety, caraway fruits contain 1.8-9.9% of essential oils consisted of about 30 compounds. Carvone and limonene accounted for the main portion, about 95%. The limonene-to-carvone ratio (%) ranged from 18.5:81.5 to 43.7-56.3.
[Determination of essential oil content in caraway (Carum carvi L.) species by means of supercritical fluid extraction, J. Sedláková, B. Kocourková, L. Lojková, V. Kubáň, Plant Soil Environ., 49, 2003 (6): 277–282] http://www.agriculturejournals.cz/publicFiles/52862.pdf
[Determination of essential oils content and composition in caraway (Carum carvi L.)., Sedlakova, J., Kocourkova, B., Kuban, V., Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 19(1), 2001, 31-36] http://agriculturejournals.cz/publicFiles/84629.pdf
The dried ripe fruits (caraway seed, Carvi fructus) and the essential oil (Carvi aetheroleum) are used as carminative, stomachic, spasmolytic, and expectorant. „The main use is to treat dyspepsia, spasms of the gastrointestinal tract and flatulence in adults and children (including babies). Caraway is added to laxatives (to prevent griping) and included in cough mixtures. Numerous other beneficial effects are claimed: appetite stimulant, breth deodorant, expectorant and tonic… The activity of caraway is ascribed to the violatile oil, of which (+)-carvone is the main constituent…“
[Medicinal Plants of the World. Ben-Erik Van Wyk and Michael Wink, Pretoria 2004, 82]
The main constituents of Carum carvi seed oil were carvone (23.3%), limonene (18.2%), germacrene D (16.2%), and trans-dihydro-carvone (14.0%). „Antibacterial activity, determined with the agar diffusion method, was observed against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial species in this study. The activity was particularly high against the genera Clavibacter, Curtobacterium, Rhodococcus, Erwinia, Xanthomonas, Ralstonia
, and Agrobacterium, which are responsible for plant or cultivated mushroom diseases worldwide. In general, a lower activity was observed against bacteria belonging to the genus Pseudomonas.“
[Antibacterial Activity of Cuminum cyminum L. and Carum carvi L. Essential Oils. Nicola S. Iacobellis , Pietro Lo Cantore , Francesco Capasso and Felice Senatore, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2005, 53 (1), pp 57–61]
„Caraway seeds are used as a flavouring of bread (e.g., rye bread), cheese, sauerkraut, candies, meat products, sauces and alcoholic liqueurs, such as the German Kümmel and as a source of carvone for cosmetics, toothpaste, chewing gum and pharmaceutical preparations. The seeds have been used in alternative medicine as a laxative, in colic treatment and as a breath freshener, even being safe to add to young childrens dishes to help digestion. The seeds have been found to have antipasmodic, carminative, emmenagogue, expectorant, galactagogue, stimulant, stomachic and tonic properties. There is an annual and a biennial caraway plant.
The latter plant is cultivated more widely as it is more productive: biennial caraway seed contains 3–7% oil;
annual caraway seed contains 2–3% oil. The main constituents of the seed are (4S)-(+)-carvone (50–70%)
and (+)-limonene (25–30%)…“
[Carvone: Why and how should one bother to produce this terpene., de Carvalho, C.C., da Fonseca, M.M.R., Food Chemistry, 95(3), 2006, 413-422]
„In human trial studies, some herbal preparations consisting predominantly caraway have shown efficacy in relieving dyspeptic symptoms. The antispasmodic effect of an alcoholic extract of caraway has shown inhibitory effects on smooth muscle contractions induced by the spasmogens, acetylcholine and histamine. This response has been evaluated to explain the beneficial effect of caraway in relieving gastrointestinal symptoms associated with dyspepsia.“
[Cuminum cyminum and Carum carvi: An update. R. K. Johri, Pharmacogn Rev. 2011 Jan-Jun; 5(9): 63–72] http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC3210012
Total fatty acid content (TFA) of three caraway seed ecotypes (Tunisian, German and Egyptian) varied from 2.9-7.3% (based on dry matter weight), the Tunisian ecotype exhibited the highest TFA proportion (7.3% DMW) than the two other ones. Petroselinic acid (C18:1n-12) was the major fatty acid in the three ecotypes, with the proportions 31.1% in Tunisian, 30.8 and 29.4% in German and Egyptian ecotype, respectively.
Essential oil yield was 1.2-1.4%, and 41 volatile compounds were identified in the seed essential oils. The main components were carvone (61.5-77.3%) and limonene (16.1-29.1%).
[Essential oils and fatty acids composition of Tunisian, German and Egyptian caraway (Carum carvi L.) seed ecotypes: a comparative study., Laribi, B., Kouki, K., Bettaieb, T., Mougou, A., Marzouk, B., Industrial Crops and Products, 41, 2013, 312-318] http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092666901200266X
„(R)-(-)-carvone and (S)-(+)-carvone caused gastric retention, reflected by decreased gastric dye emptying. These effects were accompanied by a reduction of the propulsive behaviour of the small intestine. The retarding effects of carvone on gastric emptying were also related to a decrease in the magnitude of intragastric pressure waves. The carvone-induced effects in vivo resembled those of the positive control, loperamide. In vitro, carvone relaxed sustained contractions induced by carbachol in strips of longitudinal gastric fundus and duodenum.“
[Carvone (R)‐(‐) and (S)‐(+) enantiomers inhibits upper gastrointestinal motility in mice., Silva, C., Wanderley, C.W., Lima‐Junior, F.J., Sousa, D.P., Lima, J.T., Magalhães, P.J., Palheta‐Junior, R.C., Flavour and Fragrance Journal, 30(6), 2015, 439-444]

Kohl,F.G., Die officinellen Pflanzen der Pharmacopoea Germanica, t.78 (1891-1895)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=207179
Carum carvi, Puchberg am Schneeberg 2017; author: Rolf Marschner,
www.botanische-spaziergaenge.at