Betula lenta L. - Betulaceae - sweet birch, cherry birch, black birch, Zuckerbirke
Tree, up to 20m tall, native to North America (dominant tree in the northern hardwood forests of the northern Appalachians); bark of mature trunks and branches light grayish brown to dark brown or nearly black, smooth, close, furrowed and broken into shallow scales with age; twigs with odor (and taste) of wintergreen when crushed, glabrous to sparsely pubescent, usually covered with small resinous glands, leaves ovate to oblong-ovate, 5-10cm long, base rounded to cordate, margins finely and sharply serrate or obscurely doubly serrate.
The tree „…was formerly the chief commercial source of wintergreen oil (methyl salicylate), which is distilled from its wood… Native Americans used Betula lenta medicinally to treat dysentery, colds, diarrhea, fevers, soreness, and milky urine, and as a spring tonic.“ efloras.org
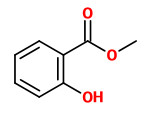 methyl salicylate (wintergreen-like)
methyl salicylate (wintergreen-like)
Sweet birch bark essential oil (fresh bark 0.29-0.39%; air-dried bark 0.6%; commercial from chopped young trees 0.23%) consists chiefly of methyl salicylate (99.8%).
[Power, B., Kleber, C., „Oil of wintergreen and oil of sweet birch.“ Pharm. Rundsch, New York, october (1895); also in: Fritzsche Brothers, Circulars of information No.7, 1894]
„In this study, the volatile compositions of the bark of B. lenta from authentic and commercial sources were assessed … The oil was dominated by methyl salicylate (93.24-99.84%)… The minor components o-guaiacol, veratrole, 2-E-4-Z-decadienal, and 2-E-4-E-decadienal were identified as natural marker compounds for authentic sweet birch oil. Surprisingly, none of the tested 27 commercial samples contained any of the identified birch markers. The detection of wintergreen markers such as vitispirane and β-dehydroelsholtzia ketone, the synthetic marker dimethyl-2-hydroxyterephthalate, and ricenalidic acid lactone suggest the addition of wintergreen, synthetic methyl salicylate, and castor oil, respectively.“
[Dosoky, Noura S., Ambika Poudel, and Prabodh Satyal. „Authentication and Market Survey of Sweet Birch (Betula lenta L.) Essential Oil.“ Plants 11.16 (2022): 2132] PDF
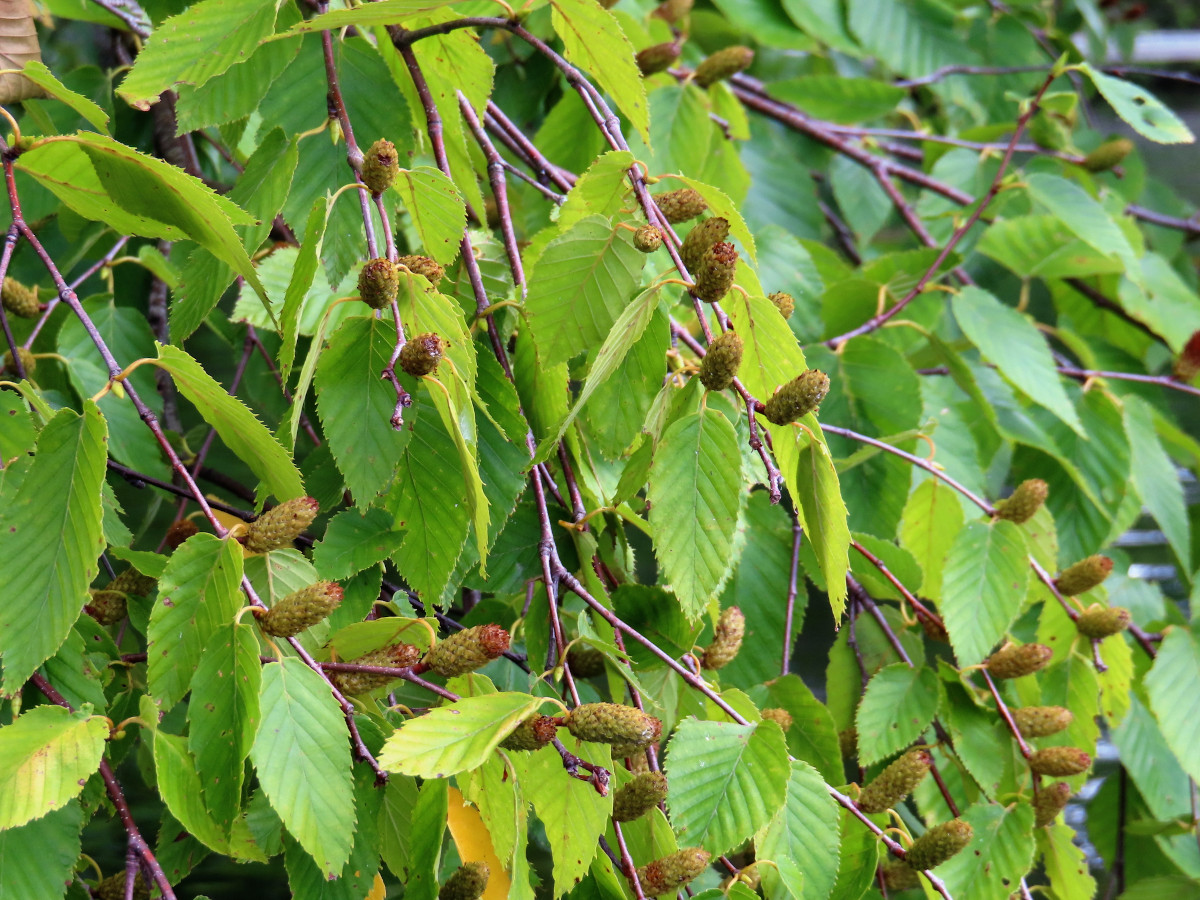

Betula lenta, Warren, USA (2025) © David P. Williams CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org

Betula lenta L., Köhler, F.E., Medizinal Pflanzen, vol.3 t.69 (1890) botanicalillustrations.org