Arnica montana L. - syn. Senecio arnica E. H. L. Krause - Asteraceae
European arnica, mountain tobacco, Leopard's Bane, Wolf's Bane, Arnika, Berg-Wohlverleih, Engelkraut, Fallkraut, Wundkraut
Upright rhizomatous perennial, up to 50cm high, native to Europe, also cultivated; stem simple, pubescent; basal rosette of ovate, hairy leaves; the stem bears only 1-2 pairs of smaller leaves; terminal flowerheads up to 6cm across, with golden-yellow three-toothed rays.
Flower heads (Arnicae flos), and tinctures, volatile oil, extracts (CO2 eg.) thereof are traditionally used to treat bruises, haematomas, sprains, burns (including sunburnes), diaper rashes. Externally applied as anti-inflammatory, wound-healing ointment, liniment or mouth wash (not to be ingested). Internal use may cause abortion, allergic reactions, contact with eyes and open wounds should be avoided.
The North American species Arnica chamissonis is another source of Arnica flowers.
[Medicinal Plants of the World. Ben-Erik Van Wyk and Michael Wink, Pretoria 2004, 53]
A standardised Arnica montana flower (origin Spain, Romania) CO2-extract is produced with helenalin and dihydrohelenalin ~0.1%, helenalin and dihydrohelenalin esters 4%, triterpenediol esters 2.0-4.5%, essential oil 0.2-0.4%.
[Arnica CO2-Extract - Approved Efficacy in Topical Treatment, May P., Cosmetic Science and Technology, 2013]
http://www.flavex.com/fileadmin/flavex.de/user_upload/Veroeffentlichungen/Arnica_Flower_CO2-Extract_-_Approved_Efficacy_in_Topical_Treatment.pdf
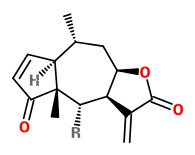
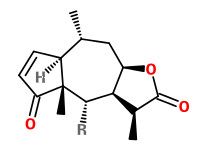
The flowers contain bitter sesquiterpene lactones (0.3-1.0%), consisting mainly of esters of helenalin and 11,13-dihydrohelenalin with short-chain fatty acids such as acetic, isobutyric, isovaleric, methacrylic and
tiglic acids. Two chemotypes are distinguished: The helenalin type is native to Central Europe and the dihydrohelenalin type (which contains only traces of helenalin) is native to Spain. Essential oil (0.2-0.35%) present consists mainly (40-50%) of fatty acids.
[Wolfgang Blaschek ed., Wichtl - Teedrogen und Phytopharmaka: Ein Handbuch für die Praxis, 2015, 89-93]

Arnica montana L., Dietrich, A.G., Flora regni borussici, vol.9 t.608 (1841)
http://plantgenera.org/species.php?id_species=89894