Aglaia odorata Lour. - Meliaceae - Chinese rice flower, Chinese perfume plant, 米仔兰 mi zi lan (chin.), Chinesische Reisblume, Chinesische Parfümpflanze
Small shrub or tree, much-branched, native to China, introduced in Southeast Asia; leaves with 3-7 obovate leaflets; flowers tiny, numerous, yellow, very fragrant. efloras.org
Regarding the chemical constituents of the essential oil from the flowers of Aglaia odorata, „21 components have been identified: hendecane, linalool, decylaldehyde, copaene, β-caryophyllen, β-humulene, β-elemene, β-selinene, humuladienone, humulene epoxide Ⅰ, tridecanic acid methyl ester, β-humulene-7-ol, β-humulene-7-ol acetate, juniper camphor, heptadecane, khusol acetate, octadecane, nonadecane, eicosane, heneicosane and docosane, among which β-humulene-7-ol is expressive of a graceful odor of Aglaia odorata.“
[A Study on the Chemical Constituents of the Essential Oils of the Flowers of Aglaia odorata Lour. Lin Zheng-hui, Hun Ying-fang, Gu Yu-hong, Acta Botanica Sinica, Vol.23(3), 1981, 7]
„The very pleasant (flowery, hay- and tea-like, woody) smelling essential oil of the flowers of Aglaia odorata Lour. (Meliaceae) consists mainly of cadinane derivatives (ca. 48%, including 27% of δ-cadinene). A main constituent is muurola-4,10(14)-dien-1β-ol (4%), accompanied by the new epimeric 1α-alcohol. Methyl jasmonates (4%) obviously make an important odour contribution.“
[Constituents of the flower essential oil of Aglaia odorata Lour. from Vietnam. Weyerstahl, P., Marschall, H., Son, P. T., & Giang, P. M., Flavour and fragrance journal, Vol.14(4), 1999, 219-224]
The small yellow flowers „… emit a strong and very refined scent much dominated by the methyl trans-(Z)-jasmonate (58.1%) and methyl cis-(Z)-jasmonate (23.2%), a scent meeting all requirements of a beautiful fragrance. No wonder that these flowers are traditionally used by Javanese ladies for parfuming their clothes and by the Chinese for scenting tea as they do with Jasminum sambac and Osmanthus fragrans.“
[Scent of a vanishing flora, Roman Kaiser, 2011, 90-91 and 307]
Twigs and leaves of A.odorata contain insecticidal cyclopentatetrahydrobenzofuran rocaglamide derivatives (activity comparable with azadirachtin). „… four new cyclopentatetrahydrobenzopyran aglain derivatives, as well as the known aminopyrrolidine odorine and odorinol, syringaresinol and flavonoid derivatives were also isolated.“
[An insecticidal rocaglamide derivatives and related compounds from Aglaia odorata (Meliaceae). Nugroho, B. W., Edrada, R. A., Wray, V., Witte, L., Bringmann, G., Gehling, M., Proksch, P., Phytochemistry, Vol.51(3), 1999, 367-376]
„The leaves and flowers of Aglaia odorata (Meliaceae) are used in China as a herbal remedy for treatment of bruises, vertigo, cough etc. and the flowers are also used for scenting tea on account of its fragrance.“ The aminopyrrolidine-diamides odorine and odorinol from A.odorata „showed remarkable inhibitory effects in two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis models induced by nitric oxide (NO) donors such as (±)-(E)-methyl-2-[(E)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-6-methoxy-3-hexenamide (NOR-1) or peroxynitrite as an initiator and TPA as a promoter.“
[Cancer chemopreventive activity of odorine and odorinol from Aglaia odorata. Inada, A., Nishino, H., Kuchide, M., Takayasu, J., Mukainaka, T., Nobukuni, Y., Tokuda, H., Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, Vol.24(11), 2001, 1282-1285]

Blanco, M., Flora de Filipinas, t.410 (1875) plantgenera.org
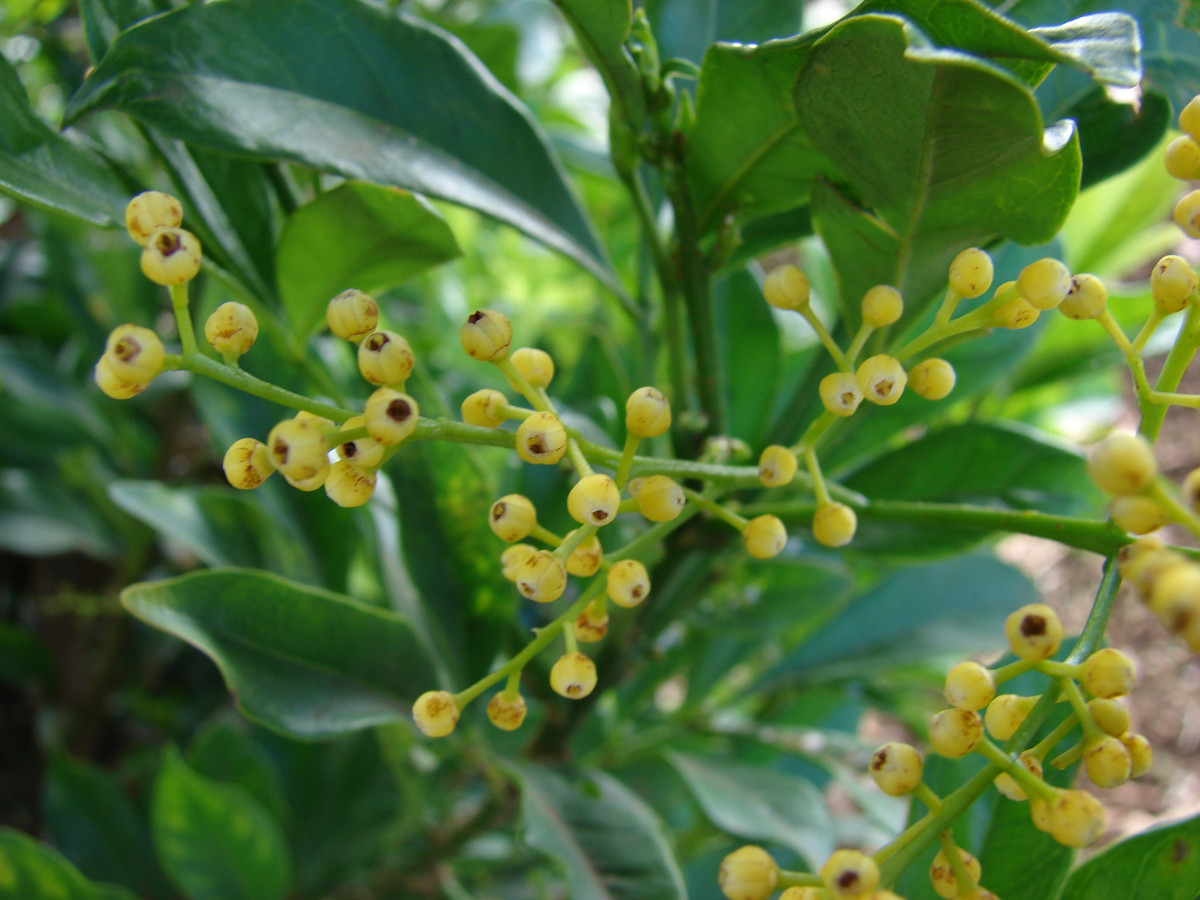

Aglaia odorata, Maui, Sun Yat Sen Park Keokea © Forest & Kim Starr (2007)
CC BY-SA 3.0 Wikimedia Commons