Aeollanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng. - syn.Aeollanthus suavis Mart.; Aeollanthus cassawa Taylor; Aeollanthus heliotropioides Oliv.; Aeollanthus glabrifolius De Wild. - Lamiaceae
catinga de mulata (brazil.), cegadinka (brazil.), macassa (brazil.), bwalangino (Nigeria); otek (Cameroon)
Sweet-Scented Aeollanthus, Süßduftender Minzenstrauch
Succulent annual herb up to 0.5m tall, native to southern tropical Africa, cultivated in Brazil; stems glabrous to hispidulous; leaves sessile or shortly petiolate; blade lanceolate to elliptic or ovate-lanceolate; flowers secund, single, closely placed, subsessile; corolla blue to purple, 4-5mm long; nutlets ovoid or oblong, smooth. JSTOR
„Widespread from Nigeria, Cameroon and Sudan through East and Central Africa south to Angola, Zambia, Botswana and northern South Africa… suaveolens: sweet-smelling or fragrant, a reference to the aromatic nature of the whole plant.“ Flora of Zambia
„Cultivated as medicinal plant against skin, ear and eye diseases in Brazil. Used as an important voodoo plant for ritual baths by the Afro-Brazilians. Grown in northern Nigeria for its very aromatic foliage, which is used to flavour soup. Employed as a medicinal plant and soap-substitute in tropical Africa. The essential oil of the plant is of potential value in perfumery. Wild distribution: Tropical Africa (Nigeria to southern Sudan and Kenya in the north to South Africa); naturalized in South America (Brazil).“
[Aeollanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng., Mansfeld's Database of Agricultural and Horticultural Plants] IPK Gatersleben
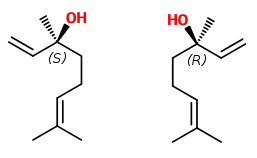
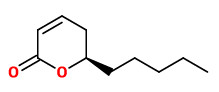
The essential oil from flowering material is dominated by linalool (41.8%), linalyl acetate (15.8%) and (E)-β-farnesene (14.0%). Oil from vegetative material contained linalool (35.5%), linalyl acetate (12.4%) and (E)-β-farnesene (17.0%). The distinct coconut-like scent is provided by δ-decalactone (traces-0.01%) and massoia lactone (0.7%) in flowering material; oil from vegetative material contained δ-decalactone (0.4%) and massoia lactone (7.0%).
[Tucker, Arthur O., Michael J. Maciarello, and Ben H. Alkire. „Essential Oil of Aeollanthus suaveolens Mart, ex Spreng.(Lamiaceae).“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 13.3 (2001): 198-199]
„Water-distilled essential oils of Aeollanthus suaveolens were analyzed by both GC and GC/MS. The major components identified in the oil of the dried plant (sample A) were (E)-β-farnesene (32.8%), linalool (31.6%), 2-decen-5-olide (massoialactone; 15.0%) and linalyl acetate (8.5%). The main constituents found in the oil of the fresh plant (sample B) were linalool (49.3%) and (E)-β-farnesene (34.9%). The compounds 2-decen-5-olide and linalyl acetate were detected only in minute quantities in the fresh plant.“
[Maia, José Guilherme S., Maria das Graças B. Zoghbi, and Eloisa Helena A. Andrade. „Essential Oils of Aeollanthus suaveolens Matt. ex Spreng.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 15.2 (2003): 86-87]
„The volatiles found in the headspace of Aeollanthus suaveolens were analyzed by solid phase microextraction coupled with GC/MS. This led to the identification of the 23 compounds. During steam distillation of the oil of A. Suaveolens, the very fragrant lactones, massoia lactone and δ-decalactone, were concentrated in the residue from which they can easily be extracted for perfumery purposes.“
[Lupe, Fernanda A., et al. „Fragrant Lactones in the Steam Distillation Residue of Aeollanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng and Analysis by HS-SPME.“ Journal of Essential Oil Research 19.3 (2007): 271-272]
„The essential oils from leaves (sample A) and flowers (sample B) of Aeolanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng were obtained by hydrodistillation and analyzed by GC, GC-MS, and chiral phase gas chromatography (CPGC). Six compounds have been identified from the essential oils, representing ca 94.3 and 93% of the oils corresponding to samples A and B, respectively. The major constituents of samples A and B essential oils were respectively, linalool (34.2%/34.9%), (-)-massoialactone (25.9%/17.0%) and (E)-β-farnesene (25.4%/29.1%). The enantiomeric distribution of the monoterpene linalool was established by analysis on heptakis-(6-O-methyl-2,3-di-O-pentyl)-β-cyclodextrin capillary column.“
[Simionatto, E., Porto, C., Stüker, C. Z., Dalcol, I. I., & Silva, U. F. D. (2007). Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil from Aeolanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng. Quimica Nova, 30(8), 1923-1925] PDF
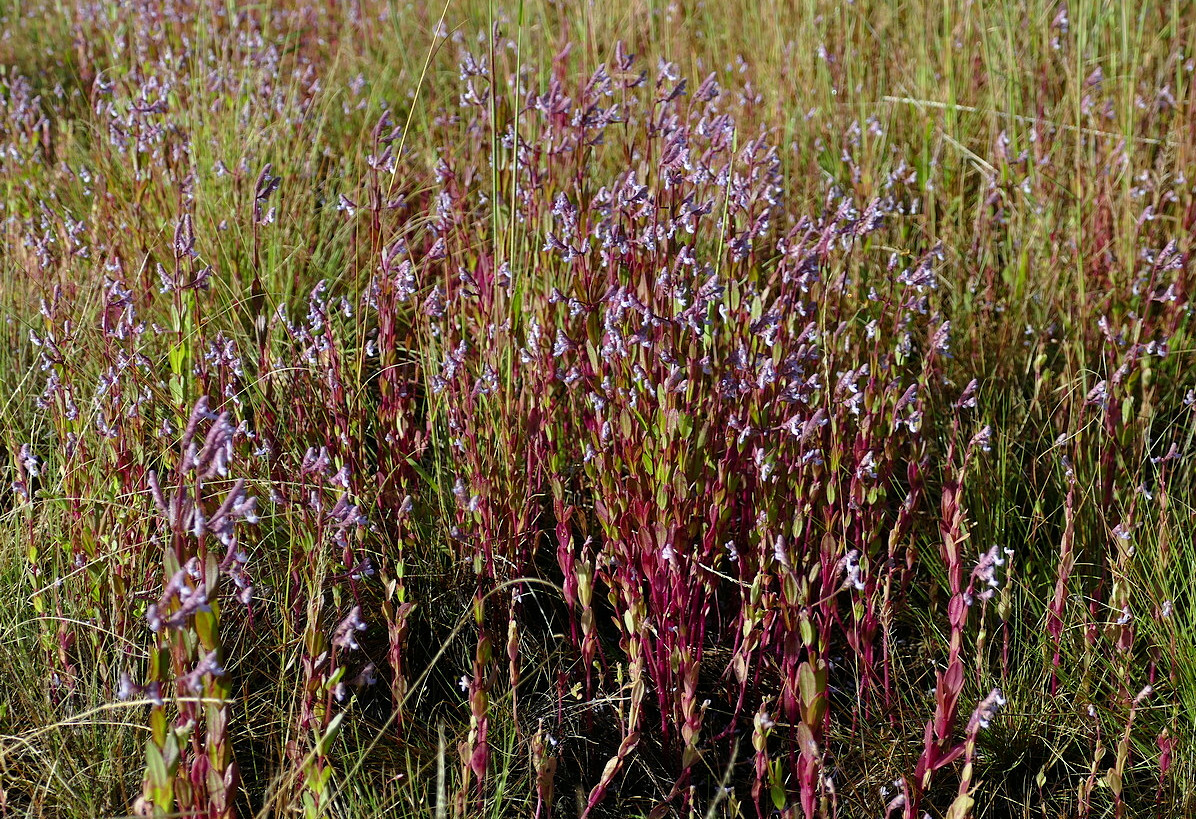

Aeollanthus suaveolens, Zambia (2024) © Jens Thalund CC BY-SA 4.0 inaturalist.org